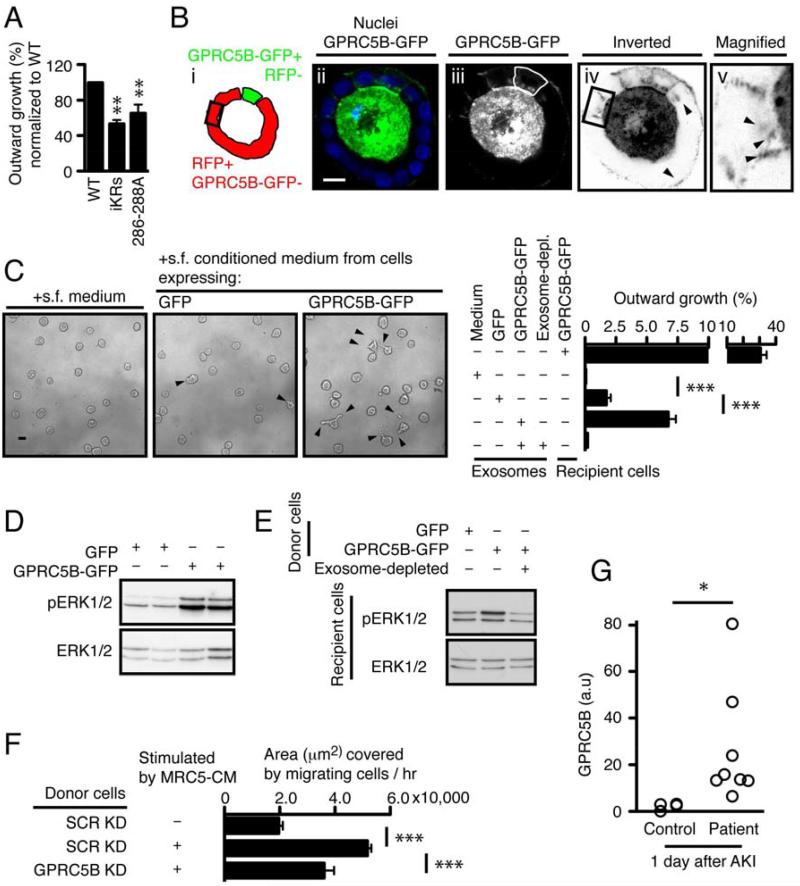
-
(A)
Quantification of outward growth in cysts expressing GPRC5B-GFP WT, iKRs, or 286-288A. The percentage of outward growth was measured as described in
Fig. 1.
-
(B)
Representative confocal images showing a mosaic cyst with MDCK cells expressing either GPRC5B-GFP or RFP. In panel iii, The GPRC5B-GFP expressing cell is outlined by a hand-drawn green line. Box outlined in black in panels i and iv marks an RFP-expressing cell that is not in contact with cells expressing GPRC5B-GFP, as determined by confocal sectioning (not shown). Panels iv and v are inverted (black to white) to better visualize the GPRC5B-GFP that is taken up by the RFP-expressing target cells. Arrowheads in panels iv and v indicate GPRC5B-GFP+ puncta taken up by RFP+ cells. Scale bar 20µm.
-
(C)
Representative images and quantification showing the effect of exosome transfer from cells expressing GPRC5B-GFP. 4-day-old cysts of WT MDCK cells in Matrigel were stimulated with indicated serum free (s.f.) medium or purified exosomes, together with 12.5 ng/ml HGF.
-
(D)
Representative immunoblots showing phosphorylated and total ERK1/2 in cysts stimulated as in (C).
-
(E)
Representative immunoblots showing augmented ERK1/2 activation in cysts that received exosomes from cells expressing GFP or GPRC5B-GFP after HGF stimulation. Note that exosome depletion abolished ERK1/2 potentiation observed in recipient cells stimulated with HGF, together with exosome transfer from cells expressing GPRC5B-GFP.
-
(F)
Wound healing due to endogenous GRPC5B carried in exosomes. MRC5 cells were grown in serum free medium and the resultant conditioned medium was centrifuged to remove any exosomes. This MRC5 conditioned medium was then added to MDCK cells grown as monolayers and expressing either shRNA for GPRC5B (GPRC5B KD) or a scrambled control (SCR KD). The conditioned medium from these MDCK cells was then subjected to centrifugation to purify exosomes. The exosomes, either GPRC5B KD or SCR KD, were then added to a second set of cultures of WT MDCK cells grown as monolayers; these cultures had an ibidi® silicone barrier to prevent growth in a gap region. The silicone barrier was removed immediately before addition of the purified exosomes. Migration was measured as the area of the gap that was covered by migrating cells over 6h.
-
(G)
Quantification of GPRC5B in human urinary exosomes. Urine was collected at the first day after critically ill subjects met pre-defined criteria for AKI and provided informed consent. Samples were processed as blinded samples to measure GPRC5B in exosomes, using immunoblotting.