Figure 1. Hierarchy of Nanocarriers.
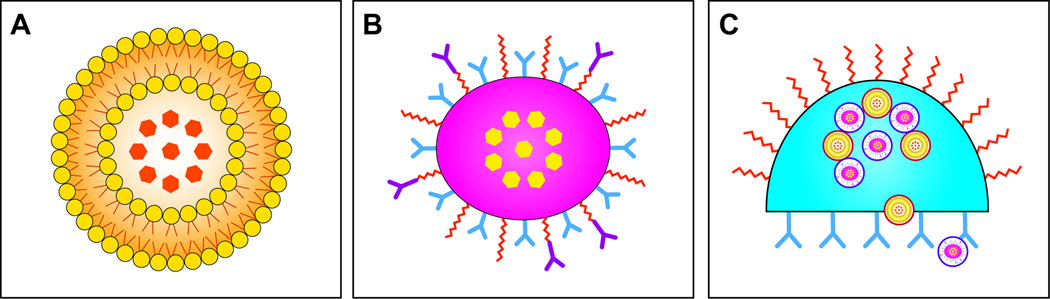
A. First-generation nanocarriers (e.g., liposomes, micelles) primary role is to enclose therapeutic or diagnostic agents and then localize in tumors by the EPR effect; B. Second-generation nanocarriers improved by incorporating further modifications allowing for specific targeting via antibodies or other recognition biomolecules or “stealthing” from MPS sequestration; C. Third-generation nanocarriers advanced the field by creating platforms capable of incorporating and preforming multiple complex functions due to their nanoscale features (e.g., multistage silicon nanocarriers ability to deploy multiple waves of nanoparticles). Reproduced with permission, © Wiley-VCH Verlay GmbH & Co. KGA [22].
