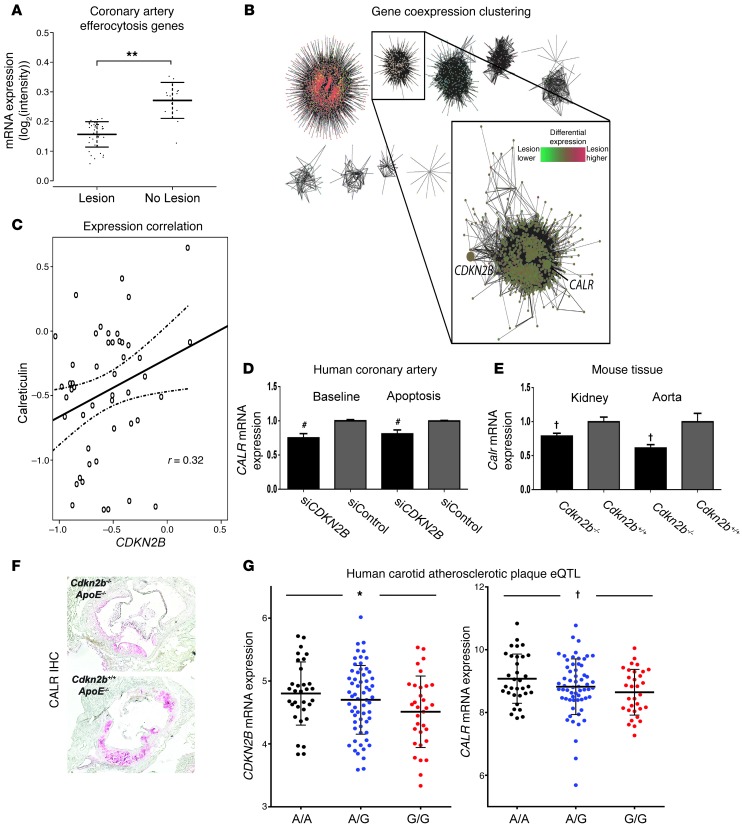
Figure 2. Loss of CDKN2B is associated with reduced expression of the key phagocyte receptor ligand calreticulin.
Weighted gene coexpression analysis of 51 HCA segments revealed that CDKN2B colocalizes with CALR in (A) local coexpression topology with efferocytosis genes that are downregulated in coronary artery samples with atherosclerotic lesions compared with those without atherosclerotic lesions (**P < 0.001), and (B) global module discovery in weighted gene coexpression analysis of 20,226 transcripts. Node color in network graph corresponds to module assignment. Inset depicts module containing CDKN2B and CALR identified via hierarchical clustering of the topological overlap between all transcript pairs. Node color in inset corresponds to differential expression of module members in coronary artery samples with atherosclerotic lesions versus those without atherosclerotic lesions. (C) CDKN2B is directly correlated with CALR expression in coronary artery sections. In all network diagrams, the edge width corresponds to the topological overlap between linked nodes. (D) A similar pattern was observed in vitro, as CDKN2B-deficient HCAMSCs expressed lower levels of CALR than control-transfected HCASMCs (siControl), both at baseline and during apoptosis. #P < 0.01. (E) Cdkn2b–/–,ApoE–/– mice also expressed less Calr than Cdkn2b+/+,ApoE–/– mice in both the kidney and aorta. (F) Semiquantitative immunostaining confirmed the reduction of Calr expression in atherosclerotic plaque from Cdkn2b–/–,ApoE–/– animals. Original magnification, ×4. IHC, immunohistochemistry. (G) eQTL analysis of 127 human carotid artery atherosclerotic plaque samples revealed that carriers of a representative 9p21 risk allele (“G” in red, relative to ancestral “A” allele in black) have simultaneous reductions in the expression of both CDKN2B (left panel, *P < 0.05) and CALR (right panel, †P < 0.03).