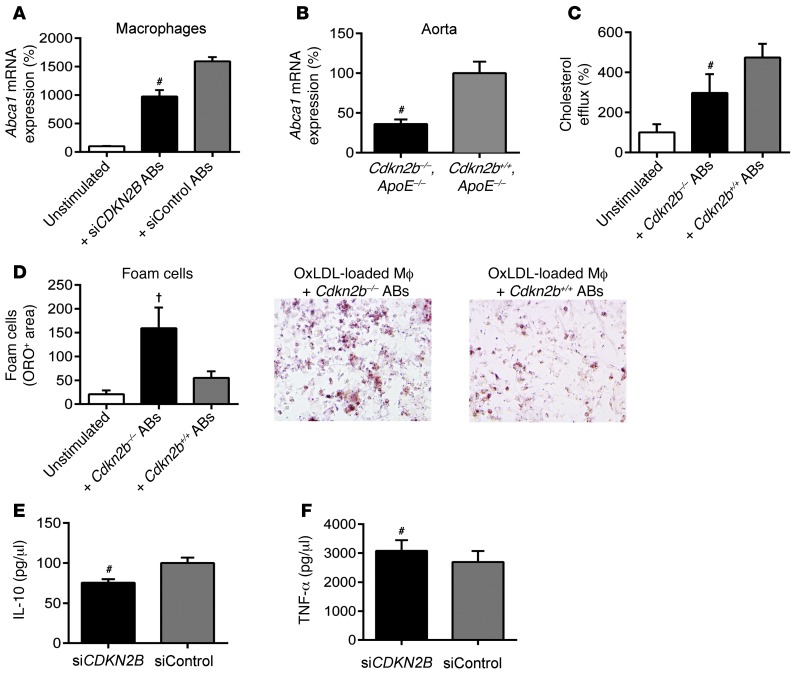
Figure 5. Macrophage biology is perturbed by interactions with apoptotic CDKN2B-deficient SMCs.
(A) Macrophages cocultured with siCont ABs (gray bar) upregulated Abca1, a key reverse cholesterol transport gene, relative to baseline (white bar). This homeostatic pathway was significantly blunted when macrophages were cocultured with siCDKN2B ABs (black bar). (B) Aortic expression of Abca1 was also reduced in Cdkn2b–/–,ApoE–/– mice relative to that in Cdkn2b+/+,ApoE–/– control mice. (C) Similarly, macrophages cocultured with Cdkn2b+/+ ABs (gray bar) displayed the expected increase in tritium-labeled cholesterol efflux relative to baseline (white bar), but a blunted response was observed for macrophages cocultured with Cdkn2b–/– ABs (black bar). (D) As a result, foam cell formation was accelerated when oxidized LDL–loaded (OxLDL-loaded) macrophages (Mf) were cocultured with Cdkn2b–/– ABs (black bar) compared with that seen in Cdkn2b+/+ ABs (gray bar). Original magnification, ×20. (E and F) Macrophages cocultured with siCDKN2B ABs secrete less antiinflammatory IL-10 and more proinflammatory TNF-α (black bars) relative to macrophages cocultured with siCont ABs (gray bars). #P < 0.01; †P < 0.03.