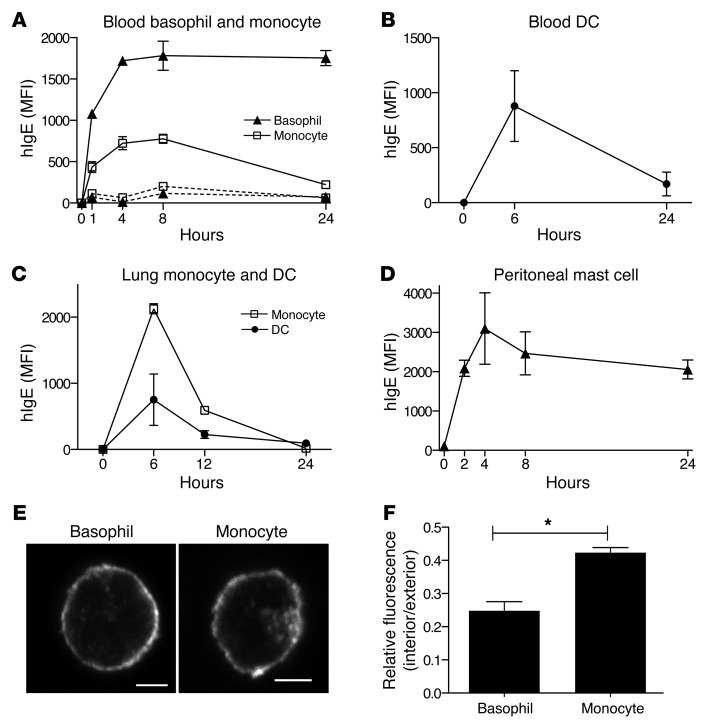
Figure 6. Human IgE injected into FCER1A-Tg mice is internalized by cDCs and monocytes in the steady state.
(A) Surface IgE levels on blood basophils and monocytes following human IgE injection. Before and at 1, 4, 8, and 24 hours after hIgE injection, Tg+ and Tg– mice were bled for flow cytometric analysis of surface IgE levels in basophils and monocytes. Data for Tg+ mice are shown in solid lines and for Tg– mice in dotted lines. Data for 3 mice from one representative experiment of 3 are presented with mean ± SEM. (B–D) Surface IgE levels on blood cDCs (B), lung DCs and monocytes (C), and peritoneal mast cells (D) of Tg+ mice following human IgE injection. At each time point following hIgE injection, mice were sacrificed and whole blood, lungs, or peritoneal lavage collected and analyzed by flow cytometry. Data for 9 mice (B), 8 mice (C), or 14 mice (D) from one representative experiment of 2 are presented with mean ± SEM. (E and F) Intracellular localization of human IgE in basophils and monocytes of FCER1A-Tg mice injected with hIgE. At 6 hours after injection, basophils and monocytes were isolated and examined for intracellular human IgE by confocal microscopy as described for Figure 3A. Original magnification, ×60; scale bars: 2.5 μm. (F) Intracellular IgE levels were quantified as in Figure 4B. Thirty images of Tg+ monocytes and basophils were analyzed. Resulting values are presented with mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.