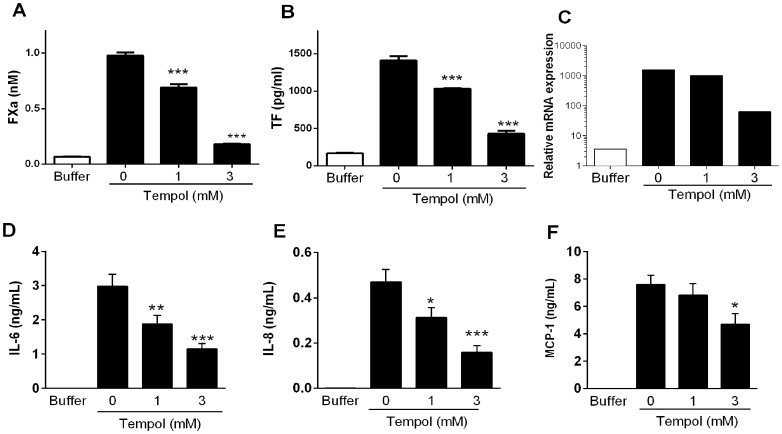
Figure 1. Tempol inhibits transcription and functional expression of tissue factor in endothelial cells, and cytokine production. A, Inhibition of tissue factor (TF) activity.
MVEC were incubated overnight with Tempol (0, 1, and 3 mM) followed by washing the wells and addition of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (200 ng/mL). A mixture containing FX and FVIIa was then added to the cells, and FXa generation was estimated in the supernatant using chromogenic substrate (S2222), as described in Materials and Methods. B, Inhibition of TF generation. Cells were incubated overnight with Tempol (0, 1, and 3 mM) followed by washing of the wells and addition of LPS (200 ng/mL) for six hours. Wells were washed and cells were lysed with 0.1% Triton X-100. The supernatant was used to detect TF antigen by ELISA. C, Inhibition of TF transcription. Cells were incubated overnight with Tempol (0, 1, and 3 mM) followed by addition of LPS (200 ng/mL) for 2 h. Cells were washed and trypsinized for extraction of mRNA. Real-time PCR of the samples was evaluated as described in Materials and Methods. The figure shows a representative result from two independent experiments. D–F, Inhibition of cytokine generation. MVEC were incubated overnight with Tempol (0, 1, and 3 mM) followed by washing of the wells and addition of LPS (200 ng/mL). After six hours, the supernatant of the cells was collected and used for detection of D, IL-6, E, IL-8, and F, MCP-1 by ELISA (n = 8). *, P≤0.05 (analysis of variance, Bonferroni post-test).