Figure 1.
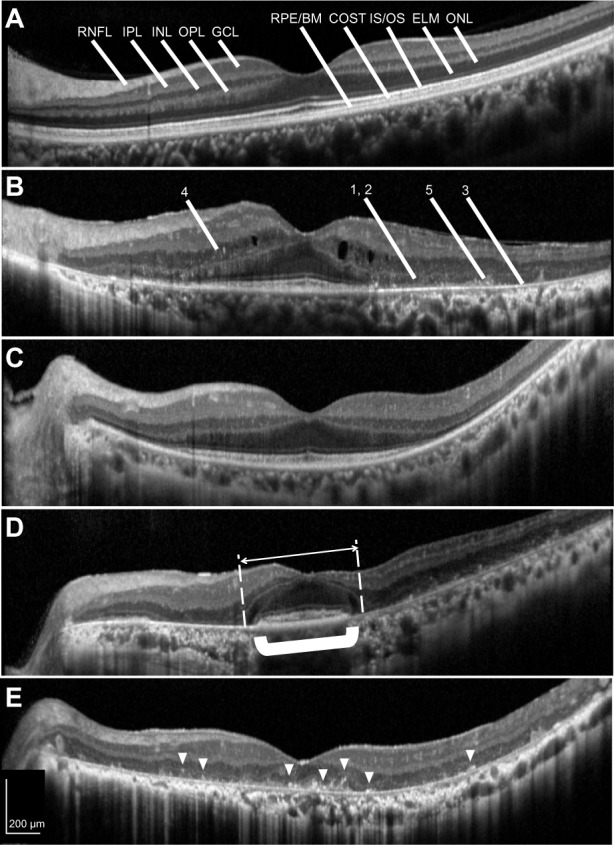
SD-OCT images of normal and RP retinas. (A) In the image of a normal eye (reduced speckle noise), the boundaries of the retinal layers are well demarcated. (B) In the image of an RP eye, some pathological findings were observed. (1) Defects of the IS/OS junction and ELM reflex, (2) thinning of the ONL, (3) thinning of the reflex of the RPE-Bruch’s membrane complex, (4) HFs in the INL, and (5) HFs in the ONL and subretinal space. (C) RP retina without HFs in the ONL. In this eye, no thinning of the reflex of RPE-Bruch’s membrane complex was observed. (D) In four cases, the ONL (white arrow) seemed to be preserved over a wider area than the RPE-Bruch’s membrane complex (shown in bold bracket). (E) RP retinas with HFs (arrowheads) in the ONL. All RP eyes with no IS/OS under the fovea had HFs in the ONL.
Abbreviations: RNFL, retinal nerve fiber layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; RPE/BM, retinal pigment epithelium and Bruch’s membrane complex; COST, cone outer segment tips; IS/OS, inner segment/outer segment junction of photoreceptors; ELM, external limiting membrane; ONL, outer nuclear layer; SD-OCT, spectral-domain optical coherence tomography; RP, retinitis pigmentosa; HFs, hyperreflective foci.
