Abstract
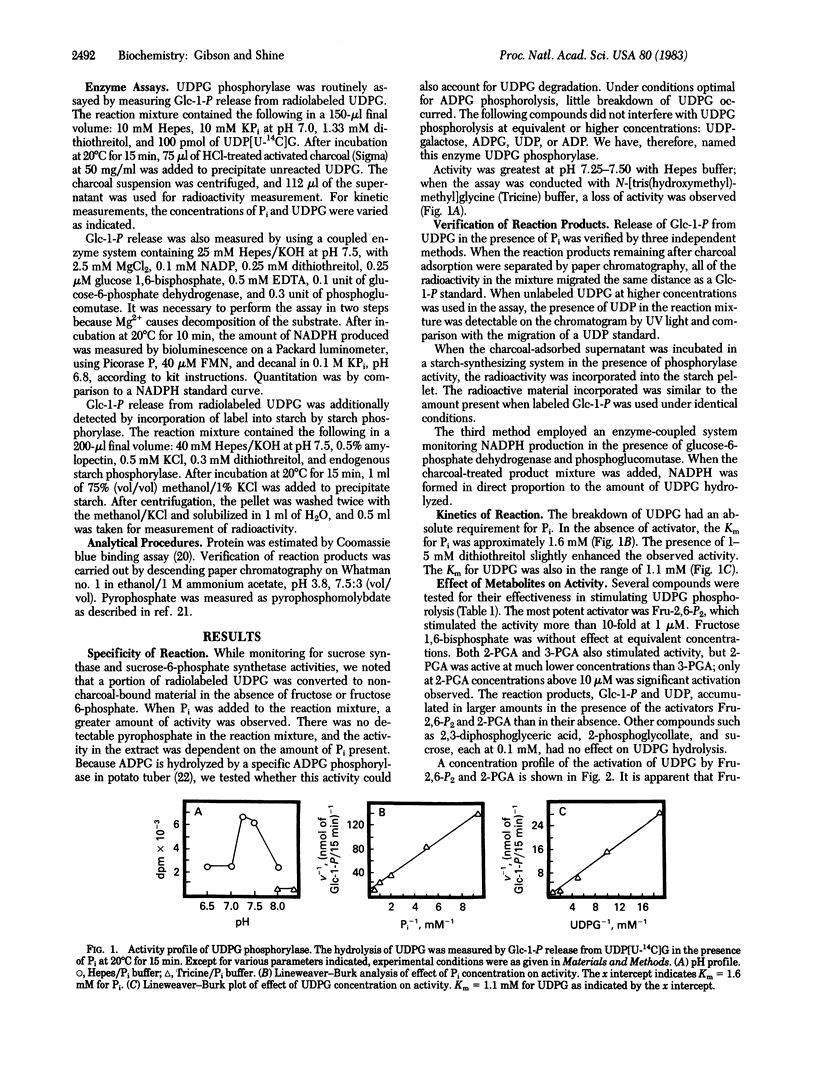
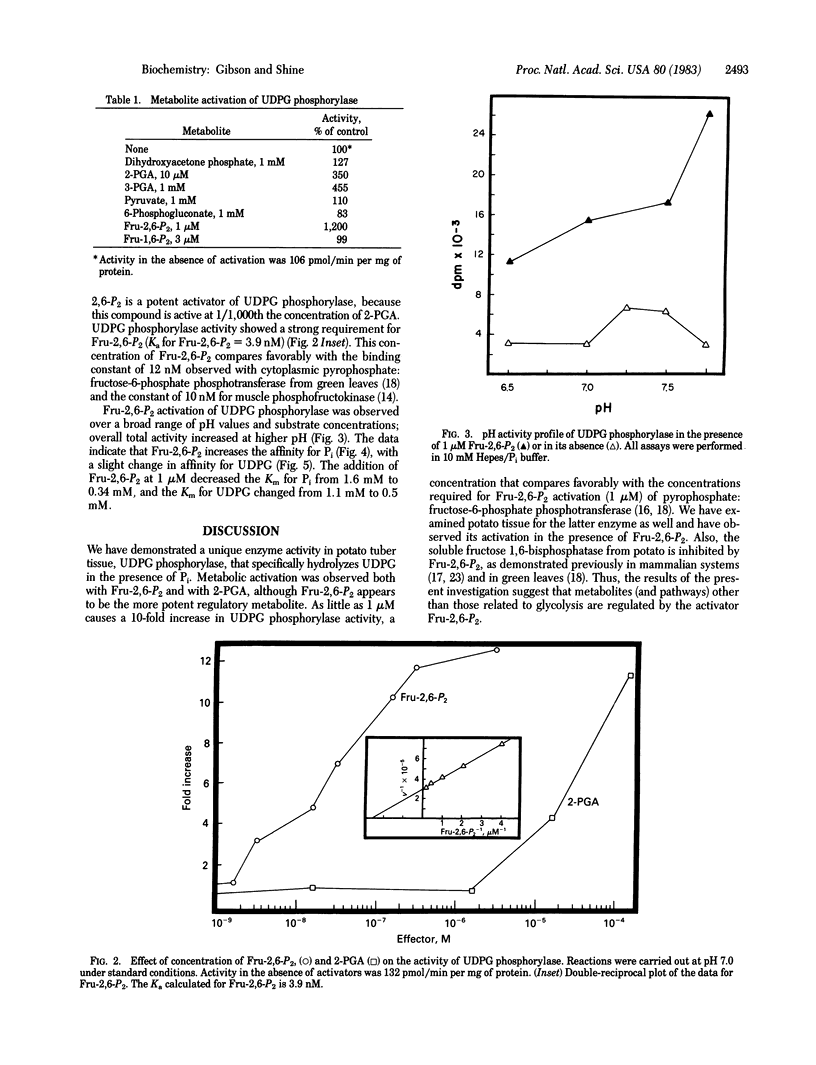
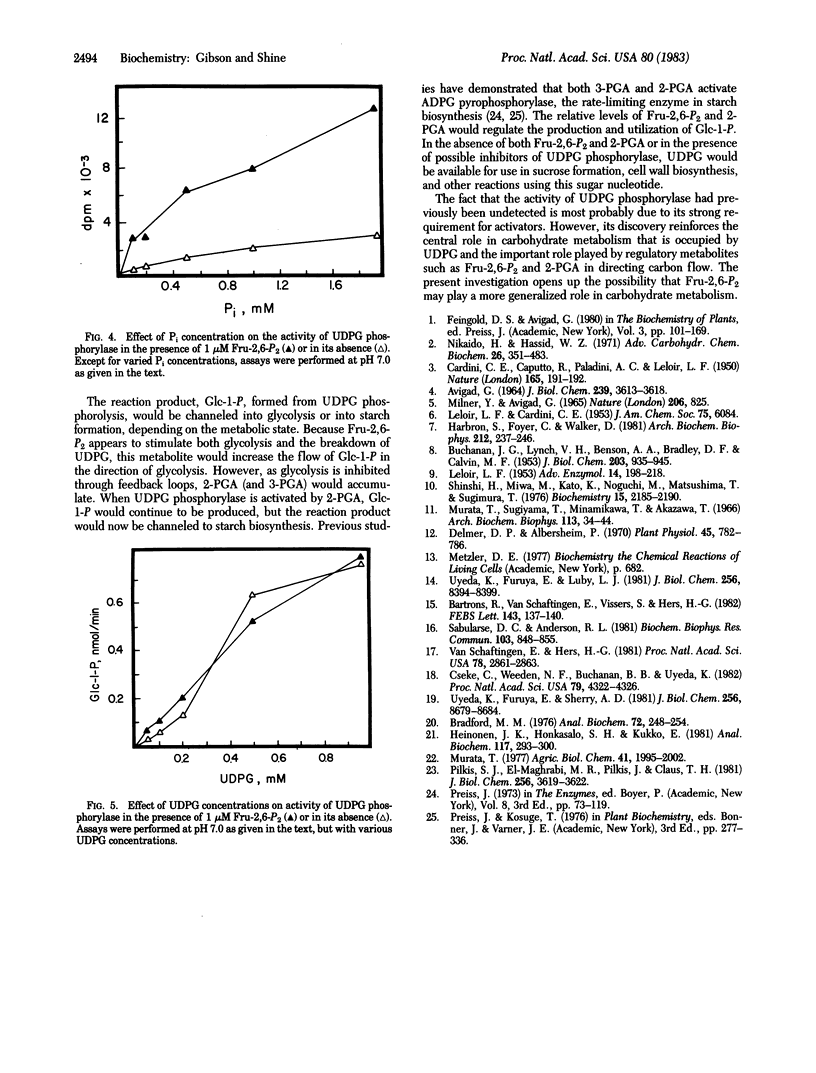
In the presence of inorganic phosphate, uridine 5′-diphosphate glucose (UDPG) is specifically hydrolyzed to glucose 1-phosphate and UDP by a unique enzyme, UDPG phosphorylase. The activity of the enzyme was maximally stimulated by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, a regulatory metabolite recently discovered in both plants and animals, and by 2-phosphoglyceric acid. At 1 μM, fructose 2,6-bisphosphate stimulated UDPG phosphorolysis 10-fold, whereas 2-phosphoglyceric acid was required at higher concentrations (100 μM) to produce a similar effect. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate appears to increase the affinity of the enzyme for inorganic phosphate, with a change in Km from 1.6 mM to 0.3 mM. The results suggest that fructose 2,6-bisphosphate participates in the regulation of other pathways of carbohydrate metabolism in addition to playing its recognized role in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.
Keywords: UDP-glucose phosphorylase, 2-phosphoglyceric acid, carbohydrate metabolism, potato
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVIGAD G. SUCROSE-URIDINE DIPHOSPHATE GLUCOSYLTRANSFERASE FROM JERUSALEM ARTICHOKE TUBERS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3613–3618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHANAN J. G., LYNCH V. H., BENSON A. A., BRADLEY D. F., CALVIN M. The path of carbon in photosynthesis. XVIII. The identification of nucleotide coenzymes. J Biol Chem. 1953 Aug;203(2):935–945. doi: 10.2172/915412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartrons R., Van Schaftingen E., Vissers S., Hers H. G. The stimulation of yeast phosphofructokinase by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 21;143(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80290-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cséke C., Weeden N. F., Buchanan B. B., Uyeda K. A special fructose bisphosphate functions as a cytoplasmic regulatory metabolite in green leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4322–4326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmer D. P., Albersheim P. The Biosynthesis of Sucrose and Nucleoside Diphosphate Glucoses in Phaseolus aureus. Plant Physiol. 1970 Jun;45(6):782–786. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.6.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbron S., Foyer C., Walker D. The purification and properties of sucrose-phosphate synthetase from spinach leaves: the involvement of this enzyme and fructose bisphosphatase in the regulation of sucrose biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90363-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinonen J. K., Honkasalo S. H., Kukko E. I. A method for the concentration and for the colorimetric determination of nanomoles of inorganic pyrophosphate. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90725-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELOIR L. F. Enzymic isomerization and related processes. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1953;14:193–218. doi: 10.1002/9780470122594.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner Y., Avigad G. Thymidine diphosphate nucleotides as substrates in the sucrose synthetase reaction. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):825–825. doi: 10.1038/206825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata T., Sugiyama T., Minamikawa T., Akazawa T. Enzymic mechanism of starch synthesis in ripening rice grains. 3. Mechanism of the sucrose-starch conversion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jan;113(1):34–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., El-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis J., Claus T. Inhibition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3619–3622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabularse D. C., Anderson R. L. D-Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: a naturally occurring activator for inorganic pyrophosphate:D-fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase in plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 15;103(3):848–855. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90888-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinshi H., Miwa M., Kato K., Noguchi M., Matsushima T., Sugimura T. A novel phosphodiesterase from cultured tobacco cells. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2185–2190. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K., Furuya E., Luby L. J. The effect of natural and synthetic D-fructose 2,6-bisphosphate on the regulatory kinetic properties of liver and muscle phosphofructokinases. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8394–8399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K., Furuya E., Sherry A. D. The structure of "activation factor" for phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8679–8684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Inhibition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by fructose 2,6-biphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2861–2863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


