Figure 5. Schematic presentation of potential mechanisms for opposite modulation of dura mater and pial/cortical vessels by GTN.
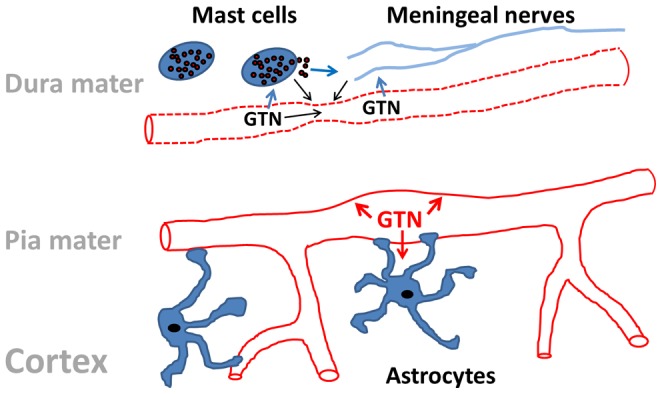
In dura mater occupied by mast cells and densely innervated by trigeminal and autonomous nerves GTN can induce vasoconstriction of small vessels either directly, or via release of vasoconstrictory agents from mast cells or through the neuronal control. The functional outcome depends on the combination of vasodilatatory versus vasoconstrictory agents and on the receptor profile. The dilatatory effect of GTN in pial/cortical vessels could be due to the direct action of this agent on the vessel wall or mediated via astrocytes releasing NO.
