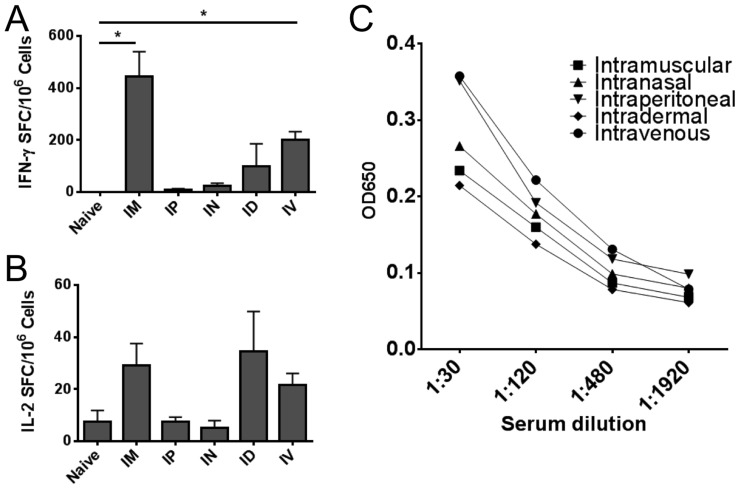
Figure 2. Intramuscular vaccination gives a superior immune response compared to other routes of injection.
BALB/c mice were vaccinated once with 109 viral particles of Ad5-Gag. Routes of injection included intramuscluar (i.m.), intraperitoneal (i.p.), intranasal (i.n.), intradermal (i.d.), or intravenous (i.v.). After 2 weeks, mice were sacrificed and spleens were removed for immune assay. Panels A and B: ELISPOT assays. A total of 2×105 fresh splenocytes were cultured in a 96 well MAIP plate coated with IFN-γ (Panel A) or IL-2 capture antibody (Panel B), in the presence of 5 ug/ml HIV-1 Gag peptide AMQMLKETI. After 18 hours plates were developed with AEC substrate and counted in an automated plate reader. Data displayed as Spot-Forming Cells (SFC) per million splenocytes. Panel C: Anti-Gag IgG ELISA. Mice were bled prior to sacrifice and serum was isolated. Serum was cultured for 2 hours at indicated dilution on ELISA plates coated with HIV-1 p55 Gag protein (10 µg/ml). Plates were washed and probed with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG antibody for 1 hour before developing with BluePhos substrate. Absorbance was measured at 650 nm.