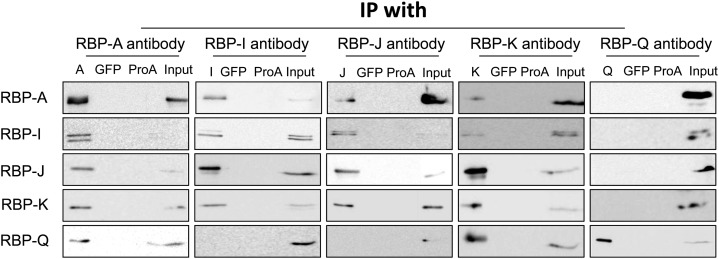
Figure 4.
Interaction of the five RBPs as viewed by Co-IP analysis. Immunoprecipitates were generated by incubating rice seed extracts with protein A conjugated with various RBP antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were then subjected to immunoblot analysis for the presence of other RBPs. Mock IPs with anti-GFP and antibody-free protein A agarose beads (ProA) were performed as negative controls. Note that RBP-A, RBP-I, RBP-J, and RBP-K are found in reciprocal IPs, while RBP-Q is only found in IPs formed by anti-RBP-A and anti-RBP-K. Note also that RBP-A and RBP-K are not found in IPs generated with anti-RBP-Q, indicating that RBP-Q is present in multiple forms, with one form being masked from interacting with its antibody when associated with RBP-A and RBP-K. Only the 36-kD polypeptide band for RBP-K is shown, as the presence of the higher molecular weight forms seen in Figures 2 and 3 was highly variable and not reproducibly detected.