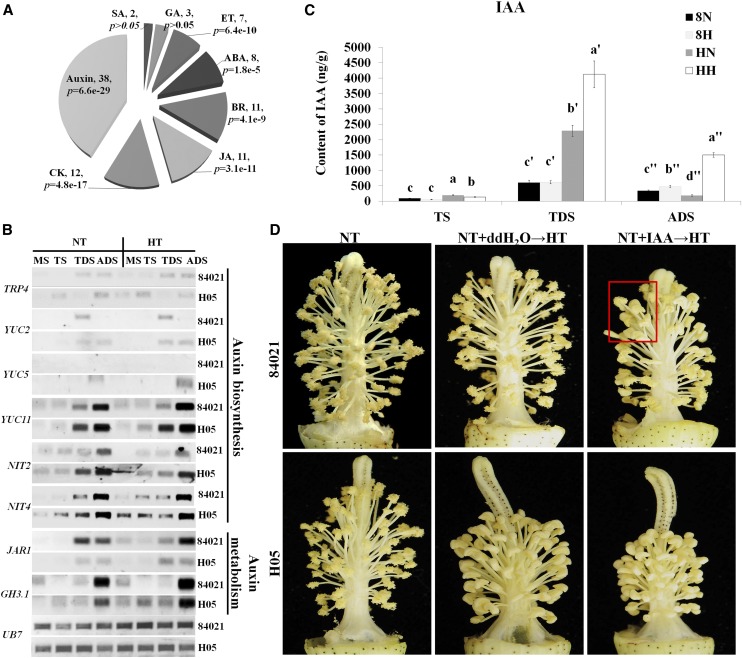
Figure 6.
Effects of the auxin signaling pathway on HT injury of cotton anthers. A, Analysis of the distribution of transcripts in plant hormone signaling pathways. BR, Brassinosteroid; CK, cytokinins; ET, ethylene; GA, GA3; JA, jasmonic acid; SA, salicylic acid. P values were determined by singular enrichment analysis (http://bioinfo.cau.edu.cn/agriGO), and the largest group was related to auxin signaling. B, RT-PCR was used to verify the detailed expression profiles of genes involved in auxin biosynthesis and catabolism. UB7, UBQUTIN7; MS, meiosis stage. C, Detection of endogenous IAA content in 84021 and H05 anthers at TS, TDS, and ADS under HT and NT conditions. H05 showed a higher background IAA concentration at TS and TDS. At all anther developmental stages, H05 showed a more sharply decreased/increased IAA concentration compared with 84021. 8N and 8H refer to 84021 under NT and HT conditions, respectively; HN and HH refer to H05 under NT and HT conditions, respectively. Data are presented as means ± se from six biologically independent experiments. Statistically significant difference analysis was performed at the respective anther developmental stage. Values not sharing a common letter are considered statistically significant (shortest significant range; P < 0.05). D, Representative anther structures are shown for each treatment. NT+ddH2O→HT and NT+IAA→HT indicate that distilled, deionized water and 10−6 m IAA, respectively, were applied four times (at days 7, 5, 3, and 0 before the temperature was increased to the stress point) to flower buds of 84021 and H05, which was followed by sustained HT damage for 7 d. The temperature was then restored to normal for 1 week, and photographs were taken. The red box indicates indehiscent anthers.