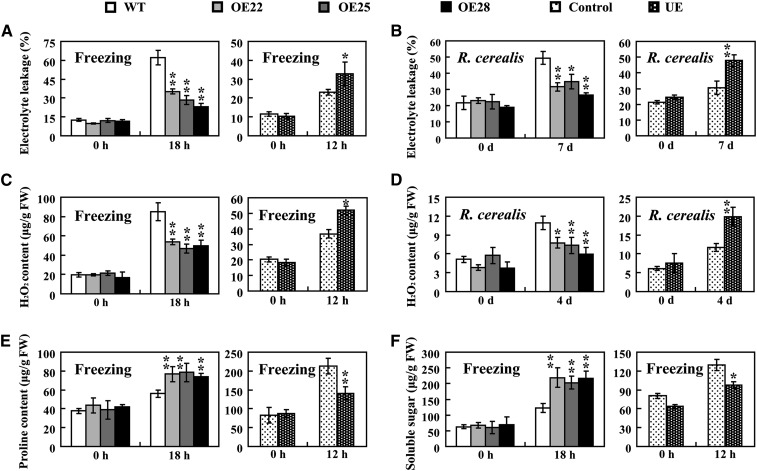
Figure 3.
Physiological traits of wild-type (WT), TaPIE1-overexpressing (OE) and TaPIE1-underexpressing (UE), and control plants. A and B, Comparison of electrolyte leakage from wild-type, OE, UE, and control seedlings with freezing treatment (A) or R. cerealis infection (B) for the indicated times. C and D, H2O2 content in wild-type, OE, UE, and control wheat plants with freezing treatment (C) or R. cerealis infection (D) for the indicated times. E and F, Free Pro (E) and soluble sugar (F) contents of OE, wild-type, UE, and control plants with or without freezing treatment. FW, Fresh weight. For freezing treatment, seedlings at the four-leaf stage from the wild-type cv Yangmai 12 and OE lines were exposed to –9°C for 18 h; UE and control plants at the four-leaf stage were maintained at –5°C for 12 h. The leaves of plants at the end of the freezing treatment or the leaf sheaths of plants after R. cerealis treatment were harvested and used for the above assays. Significant differences between the OE and wild-type plants or the UE and control plants under the same conditions were analyzed based on three replications (Student’s t test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). Error bars indicate se.