Figure 6. Effect of NF-κB inhibitors on apoptosis of human eosinophils in the presence of TNF-α.
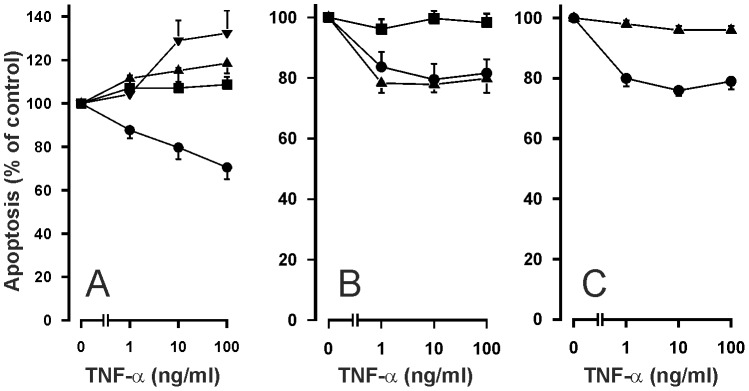
The effects of NF-κB inhibitors A. PDTC (▪ 1 µM; ▴ 10 µM; ▾100 µM), B. gliotoxin (▪ 0.9 µg/ml) and the inactive methylgliotoxin (▴ 0.9 µg/ml) and C. an inhibitor of IκB kinases-1 and -2, BMS-345541 (▴ 10 µM) on TNF-α-induced inhibition of apoptosis in isolated human eosinophils after 40 h culture. In each figure, the concentration-response curve of TNF-α in the absence of inhibitors (solvent control) is indicated by (•). Apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry measuring the relative DNA content of propidium iodide-stained eosinophils. Each data point represents the mean ± SEM of 6-9 independent determinations using eosinophils from different donors. In A, the percentage of apoptotic eosinophils in the absence of TNF-α and PDTC was 57.4±5.5 and in the presence of PDTC it was 63.6±11.0 (1 µM; P>0.05), 49.1±8.0 (10 µM; P>0.05) and 33.1±2.7 (100 µM; P<0.05). In B, the percentage of apoptotic eosinophils in the absence of TNF-α and gliotoxin was 32.7±5.2 and in the presence of gliotoxin (0.9 µg/ml) it was 77.1±4.3 (P<0.001). In C, the percentage of apoptotic eosinophils in the absence of TNF-α and BMS-345541 was 53.5±2.3 and in the presence of BMS-345541 (10 µM) it was 88.2±1.6 (P<0.001).
