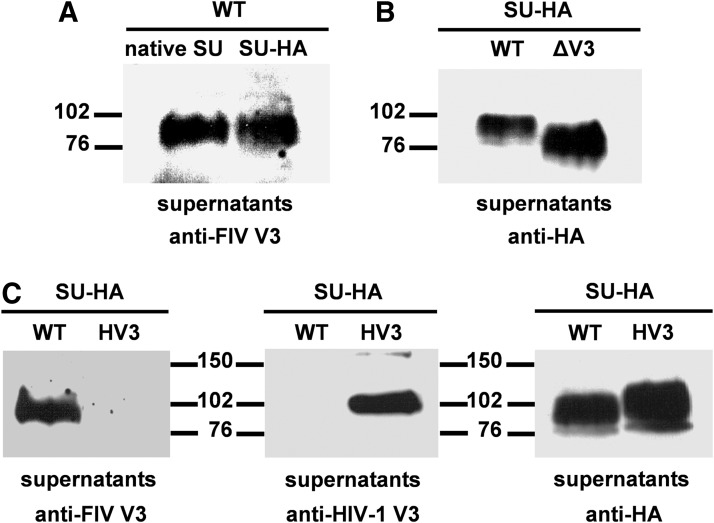
FIG. 2.
Expression in human cells of wild-type (WT), mutant (ΔV3), and chimeric (HV3) SU glycoproteins C-terminally tagged with the HA epitope. (A) 293T cells were transfected with the FIV proviral DNA and 48 h posttransfection the culture medium was recovered and clarified as described in Materials and Methods. In parallel, 293T cells were first infected with the recombinant vaccinia virus expressing the T7 RNA polymerase and then transfected with the SU-HA-expressing construct. Thirty hours postinfection, the cell-free supernatant was harvested. Aliquots of both cell culture supernatants were subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotted with the anti-FIV V3 monoclonal antibody (MAb) so as to detect in these samples the native FIV SU and the wild-type SU glycoprotein carrying the HA epitope at its C-terminus. (B) The wild-type (WT) and mutant (ΔV3) SU-HA glycoproteins were expressed in 293T cells as explained in Materials and Methods. The SU proteins secreted into the cell culture media were visualized by western blotting using the anti-HA MAb. (C) The clarified supernatants from 293T cells expressing either the wild-type (WT) or the chimeric (HV3) SU-HA glycoproteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with MAbs directed to the FIV V3, the HIV-1 V3, or the HA epitope. The positions of the molecular weight standards (in kDa) are indicated.