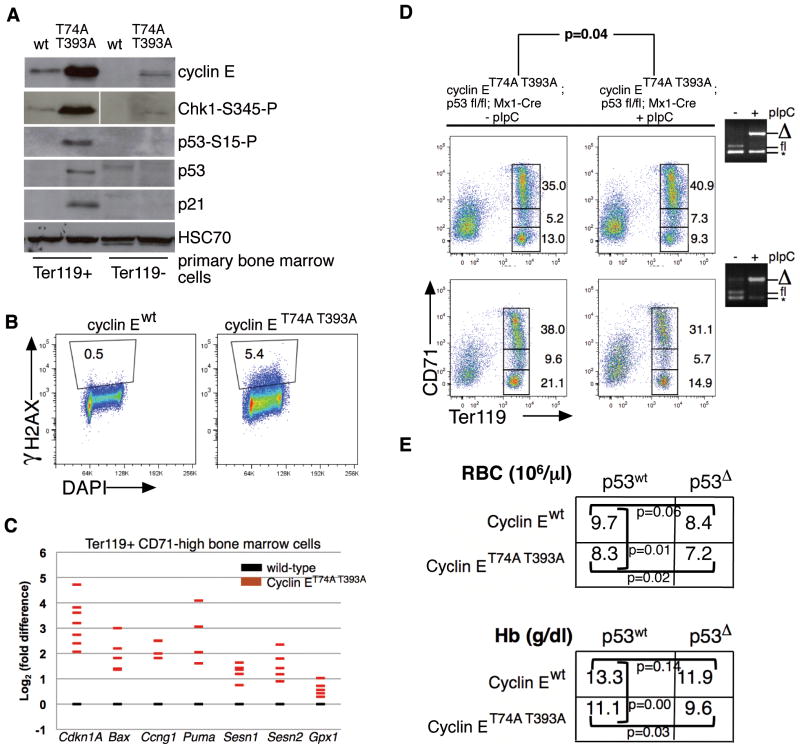
Figure 3. Dysregulated cyclin E in bone marrow erythroid progenitor cells activates p53 and the DNA damage response pathway.
(A) Immunoblot analyses for cyclin E and components of the p53-dependent DNA damage response were performed using primary bone marrow cell lysates prepared after immunomagnetic separation based on Ter119 expression. HSC70 is shown as loading control; phospho-Chk1 detection was performed using same lysates as rest of immunoblot, but these were electrophoresed separately. (B) DNA damage foci were enumerated in primary Ter119+ bone marrow cells of the indicated genotypes using serine 139-phosphorylated H2AX (γH2AX) detection by flow cytometry. Shown is a representative comparison from two independent experiments. (C) Expression of the indicated p53 gene targets in Ter119+ CD71-high erythroid cells was measured by RT-PCR. Each colored bar represents averaged value of triplicate RT-PCR assays from a single knock-in mouse, expressed relative to expression in cells from age- and sex-matched wild-type controls. (D) Erythroid maturation was studied in ten wild-type recipient mice transplanted with 1×106 cells of the indicated genotypes and 5×105 wild-type (CD45.1) bone marrow cells. Five weeks following engraftment (equivalent for wild-type and knock-in donor cells), half the recipient mice were treated with pIpC, and sixteen weeks later, recipients were euthanized for study. Ter119 vs. CD71 immunophenotyping profiles from bone marrows are shown for two representative sets of mice along with PCR genotyping (far right) of bone marrow cells demonstrating efficient excision of floxed p53 allele following pIpC injections (* - non-specific amplicon generated by PCR). The p-values are calculated from paired t test comparing ratios of low CD71-, Ter119+ and high CD71-, Ter119+ erythroid progenitors. (E) Mean peripheral red blood cell counts and hemoglobin concentrations are shown for recipients of purified hematopoietic stem cells isolated from donor mice, three months following transplantation (n=24). Engraftment measured by peripheral blood CD45.2-positive cell enumeration was found to be comparable across all donor HSC groups (70–87%).