Figure 8. Proposed model depicting interplay between SCFFbw7-dependent cyclin E control and regulation of ROS during terminal erythroid cell maturation.
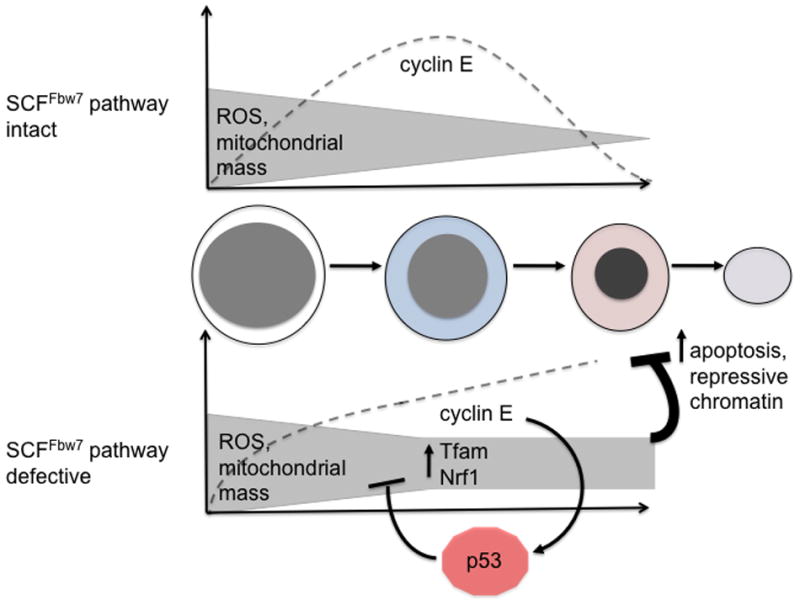
Dashed lines represent normal trend in expression (top) of cyclin E protein during terminal erythroid maturation (morphologies depicted from left to right: proerythroblast, basophilic erythroblast, orthochromatic erythroblast, and reticulocyte) and its pathological expression (bottom) in the setting of Fbw7 loss-of-function. Activation of p53 in response to dysregulated cyclin E expression is represented as well as its activity to counteract ROS through induction of several downstream target genes with anti-oxidant functions.19,33
