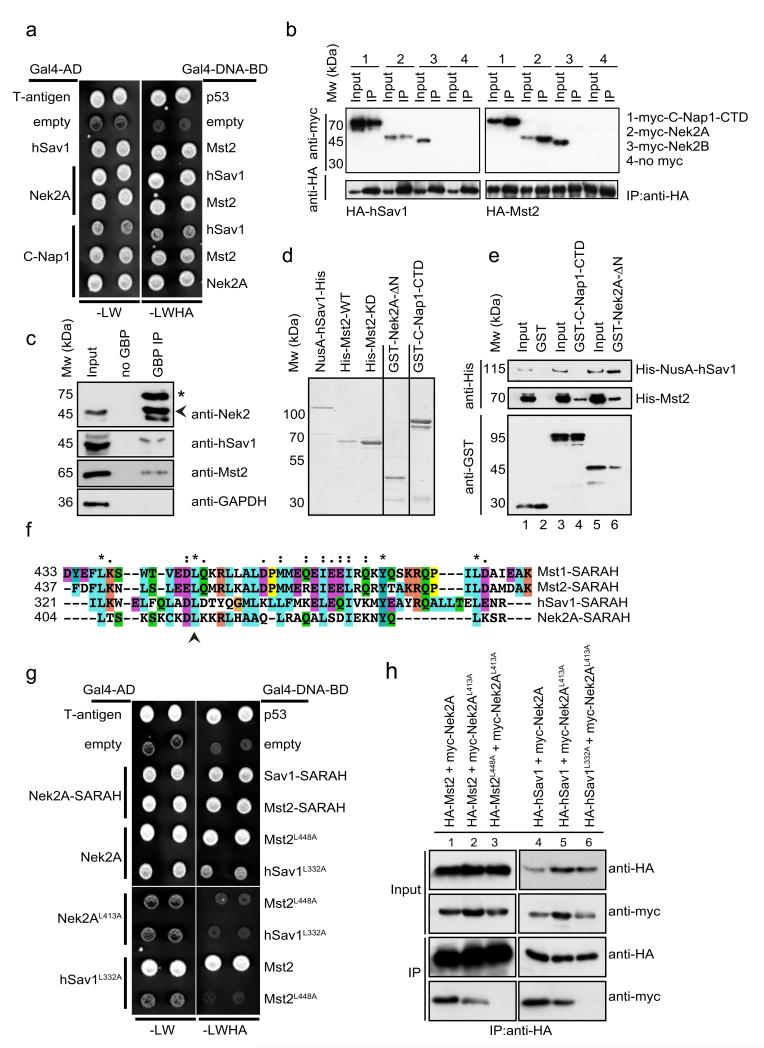
Figure 1. Interactions between Nek2A, C-Nap1, hSav1 and Mst2.
a- Yeast two-hybrid analyses of the interactions between hSav1, Mst2 and Nek2A. Yeast cells with either Gal4-DNA-BD or Gal4-AD plasmid derivatives were mated on YPD plates and selected for –LW and –LWHA plates. Growth on –LW plates indicates mating and on –LWHA plates interaction of bait and prey encoded proteins. Colonies from non-interactors (e.g. empty plasmids) appear darker on –LW plates because cells did not express ADE2 and therefore accumulate a red pigment.
b- Co-IP of hSav1, Mst2, C-Nap1 and Nek2. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with the indicated constructs followed by anti-HA immunoprecipitation. Immunoprecipitated proteins were analysed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting.
c- Co-IP of endogenous hSav1, Nek2A and Mst2. Extracts of LAP-Nek2A cell line which have near-endogenous levels of Nek2A were prepared and Nek2A was immunoprecipitated with GFP-binder protein (GBP) coupled (GBP IP) or uncoupled (no GBP) to NHS-activated sepharose beads. The asterisk indicates LAP-Nek2A and the arrowhead Nek2. Of note is that LAP-Nek2A is difficult to detect in cell extracts with anti-Nek2 antibodies without enrichment by immunoprecipitation because of its low expression. LAP-Nek2A also immunoprecipitates endogenous Nek2 due to dimerization of Nek2 45.
d- NusA- and 6His-tagged hSav, GST-tagged C-Nap1-CTD and Nek2-ΔN were purified from E. coli, whereas wild-type and kinase-dead versions of Mst2 (Mst2-KD: K56R) were purified from Sf21 insect cells. Recombinant proteins were analysed by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Simply Blue Safe staining (Invitrogen).
e- Direct interactions between hSav1, Mst2, Nek2A and C-Nap1. Purified, recombinant GST-tagged truncations of C-Nap1 and Nek2A were incubated with recombinant His-tagged hSav1 or Mst2. C-Nap1 and Nek2A proteins were precipitated with glutathione sepharose beads and bound proteins were analysed by immunoblotting.
f- Presence of a putative SARAH domain in Nek2A. Sequence alignment of the C-terminal coiled-coil of Nek2A with the SARAH domains of hSav1 and Mst1/2 kinases.
g- Mutations in the SARAH domains of Nek2A, Mst2 and hSav1 impair interactions. Yeast two-hybrid analyses of indicated Leu-Ala mutants.
h- Myc-tagged Nek2A constructs together with HA-tagged hSav1 or Mst2 constructs were coexpressed in HEK293 cells. HA-tagged proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies. Co-immunoprecipitation of myc-tagged proteins was determined by immunoblotting.