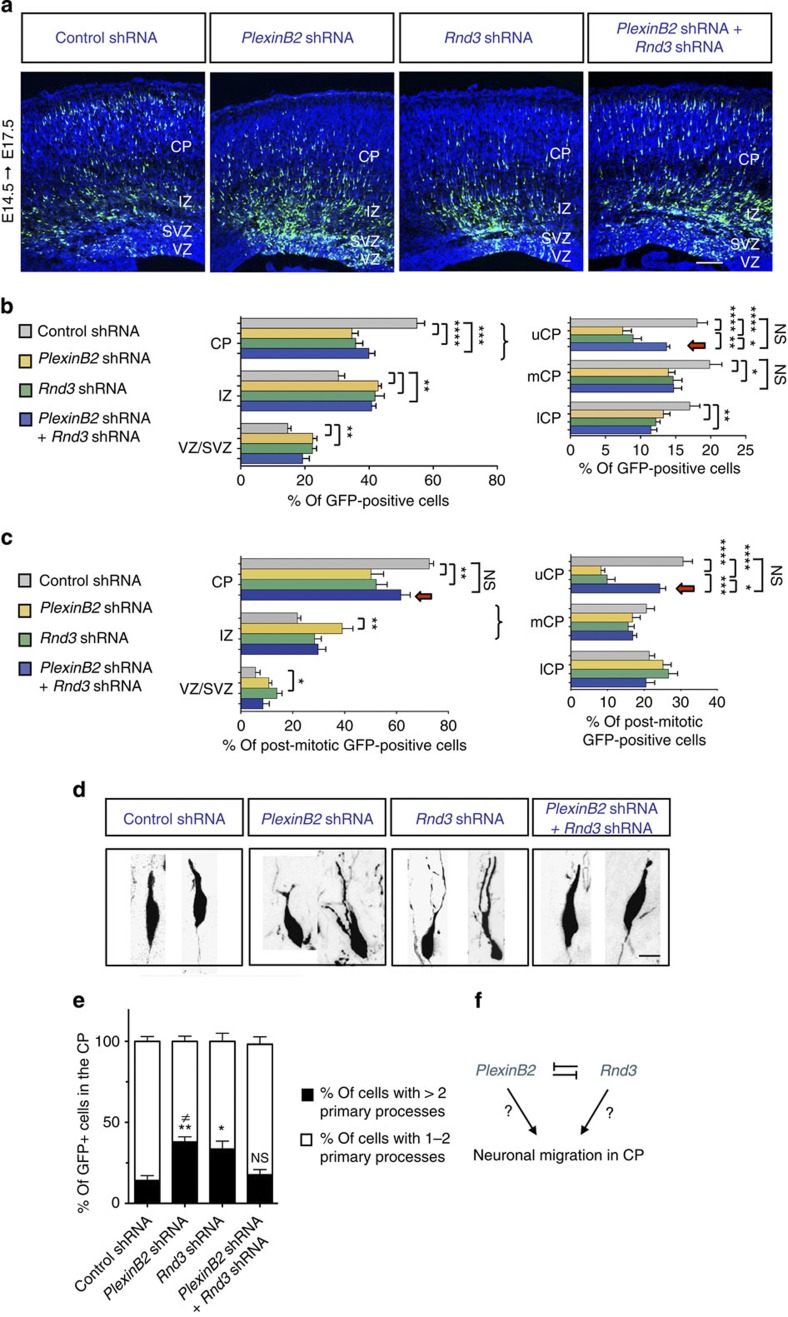
Figure 3. Plexin B2 and Rnd3 antagonize each other’s activities in radially migrating neurons.
(a) Mouse embryonic cortices electroporated with control shRNA, Plexin B2 shRNA, Rnd3 shRNA or Plexin B2 and Rnd3 shRNAs together at E14.5 and analysed 3 days later. The migration defect produced by Rnd3 or Plexin B2 silencing was partially rescued by the concomitant knockdown of the two genes. Scale bar, 200 μm. (b) The quantification graph compares the distribution of GFP+ cells in the different electroporation experiments. The CP is further subdivided into lower CP (lCP), median CP (mCP) and upper CP (uCP). The red arrow in the quantification graph highlights the migratory rescue in the uCP. Mean±s.e.m. from six sections prepared from three different experiments; one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001; NS, not significant. (c) The graph reports the distribution of post-mitotic (GFP+/ki67−) cells in the different experiments. The red arrows indicate the migratory rescue when both Plexin B2 and Rnd3 are silenced. Mean±s.e.m. from six sections prepared from three different experiments; one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001; NS, not significant. (d) Morphology of radially migrating neurons electroporated with the different constructs as indicated. Aberrant shapes were observed in both Plexin B2-silenced neurons and Rnd3-silenced down cells. Scale bar, 10 μm. (e) Quantification of the morphologies of electroporated cells in the CP. The percentages represent the proportion of cells exhibiting more than two primary processes (that is, attached to the cell body). n>150 cells from three different brains. One-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test; *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 compared with control, ≠P<0.05 compared with double knockdown. (f) Drawing of the genetic interaction between Plexin B2 and Rnd3. The two factors antagonize each other’s activities in the control of neuronal migration and morphology in the CP.