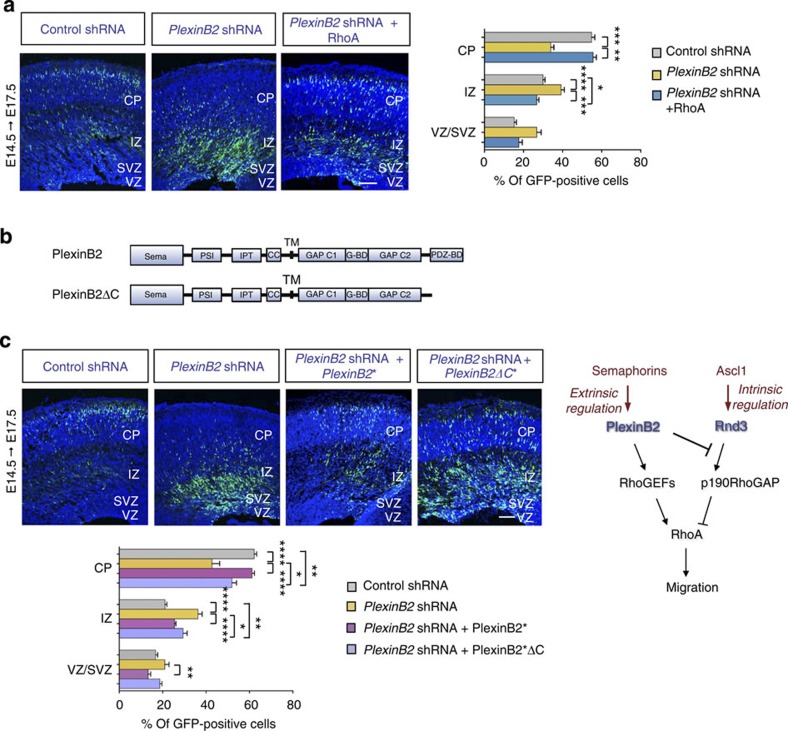
Figure 6. Plexin B2 activates RhoA in the cortex in part by recruiting RhoGEFs.
(a) The migration defect induced by Plexin B2 shRNA electroporation was rescued by co-electroporation of a RhoA expression vector. The graph shows the distribution of electroporated GFP-positive cells per cortical compartment in the different conditions. Mean±s.e.m. from six sections prepared from three different experiments; one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post-hoc test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001. Scale bar, 200 μm. (b) Schematic representation of the different domains of the Plexin B2 protein. The PDZ-binding domain (PDZ-BD) at the C terminus of wild-type Plexin B2 has been removed in the Plexin B2 C-terminal deletion mutant (PlexinB2ΔC). Sema: Sema domain; PSI: plexin, semaphorin and integrin domain; IPT: Ig-like, plexin and transcritpion factor domain; CC: convertase cleavage site; TM: transmembrane domain; GAP C1/C2: segmented GTPase activating protein (GAP) domain; G-BD: GTPase binding domain; PDZ-BD: PDZ-binding domain. (c) Images of electroporated cortices and quantification graph show that PlexinB2ΔC* ameliorates the defects induced by Plexin B2 knockdown, although not as efficiently as wild type PlexinB2*. The star (*) indicates that the constructs carry mutations conferring RNAi resistance. Mean±s.e.m. from six sections prepared from three different experiments; one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ****P<0.0001. Scale bar, 200 μm. (d) Model of how the Ascl1-Rnd3 and Semaphorin-PlexinB2 interact to regulate RhoA activity in cortical neuronal migration. On the one hand, Ascl1-Rnd3 maintains low background levels of RhoA activity by interacting with p190RhoGAP. On the other hand, upon extracellular activation, Plexin B2 promotes RhoA activation by two mechanisms, blocking Rnd3 interaction with p190RhoGAP and directly recruiting RhoGEFs.