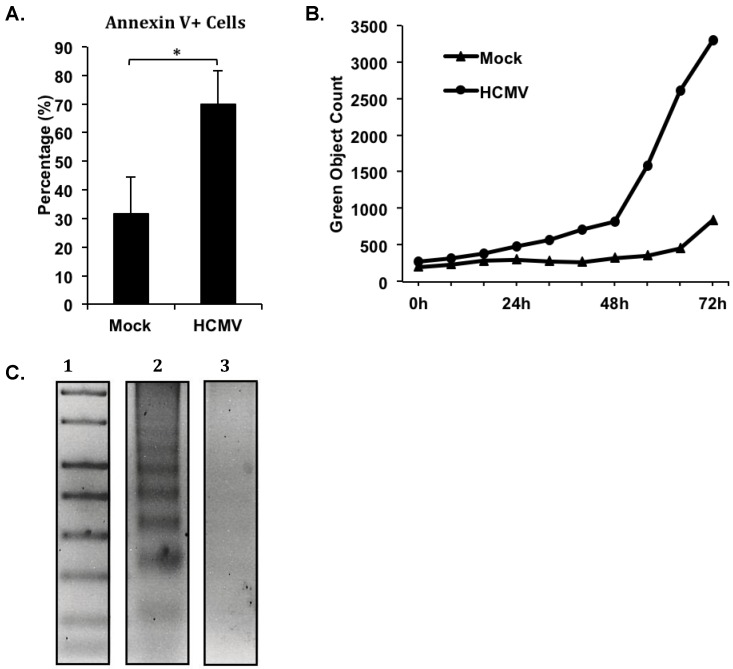
Figure 1.
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) induces the upregulation of apoptosis-associated markers in the absence of increased apoptosis. Primary human peripheral blood monocytes were isolated as previously described [22,44]. Monocytes were mock- or HCMV-infected (Towne/E p.41 MOI 5) for 72 hours at 37 °C in 5% CO2, and kept either in suspension (A and C) or adherent in a 96 well plate (B) in 1% human serum RPMI 1640 (Cellgro). (A) At 72 hours post infection, monocytes were harvested, stained with Annexin V-FITC and PI, and analyzed by flow cytometry. The average percentage of Annexin V positive, PI negative cells in each sample from three separate donors is represented. Student’s paired t-test was used to determine statistical significance (* p < 0.05). (B) At the time of infection, triplicate samples were treated with 5 μM CellPlayer™ 96-Well Caspase-3/-7 reagent. Samples were placed in an IncuCyte™ Zoom live imaging system at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Phase contrast and green fluorescence images of each sample at identical areas were acquired every six hours for 72 hours. The number of green objects detected per image was normalized to the number of cells detected by phase contrast per respective image. The resulting green object count for each sample is represented. (C) At 120 hours post infection, fragmented DNA was harvested from samples using a Calbiochem® Suicide Track™ DNA Ladder Isolation kit. Isolated DNA was run on a 1.5% agarose/TAE gel at 50 constant volts. The gel was then stained with ethidium bromide and apoptotic DNA was visualized by UV illumination. All samples were run on the same gel under the same conditions; however, a lane containing an irrelevant treatment option was removed for the final figure. Lane 1 contains the 1 kb DNA standard ladder, Lane 2 contains DNA from mock-infected monocytes, and Lane 3 contains DNA from HCMV-infected monocytes.