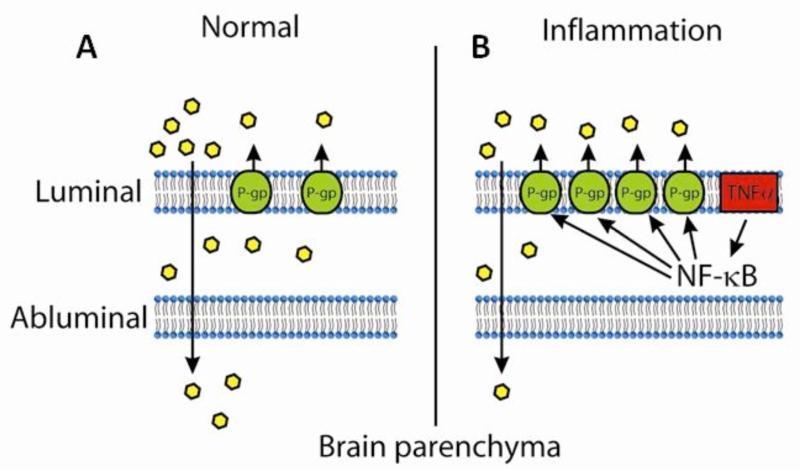
Fig. (4).
Schematic representation of regulation of P-gp during inflammation: Under normal physiological conditions, P-gp present on the luminal side of the BBB limits the brain uptake of drugs. In inflammatory diseases, TNF-α activates NFκB, which leads to transcriptional activation of P-gp. This leads to increased activity of P-gp and in turn causes further decrease in the brain penetration of drugs.