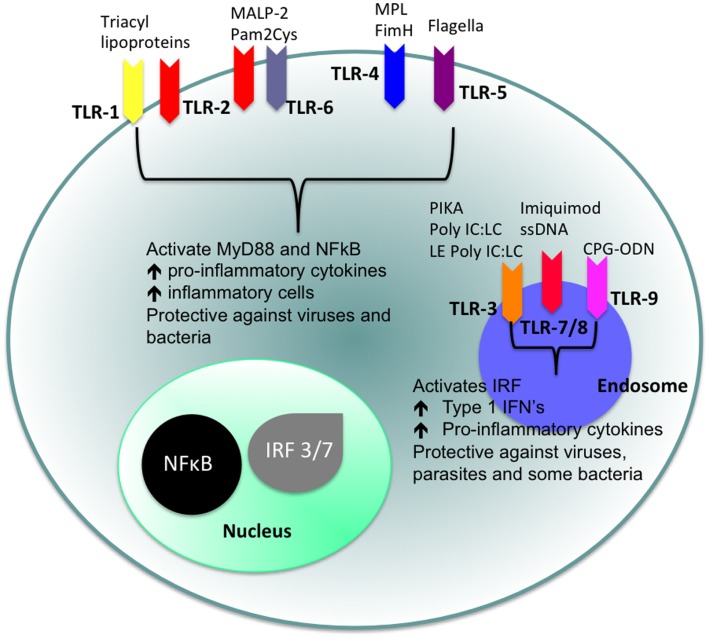
Figure 1.
Cellular location of TLRs and the identity of their ligands/agonists. The stimulation of surface TLRs (TLR-2, TLR-4, and TLR-5) with appropriate ligands results in the activation of NFκB. The ensuing increase in levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the influx of inflammatory cells then provides an environment, which protects against both virus and bacterial challenge. Activation of intracellular TLRs (TLR-3, TLR-7, TLR-8, and TLR-9) leads to IRF activation and the production of Type 1 IFNs and pro-inflammatory cytokines, again providing an environment not conducive for pathogens.