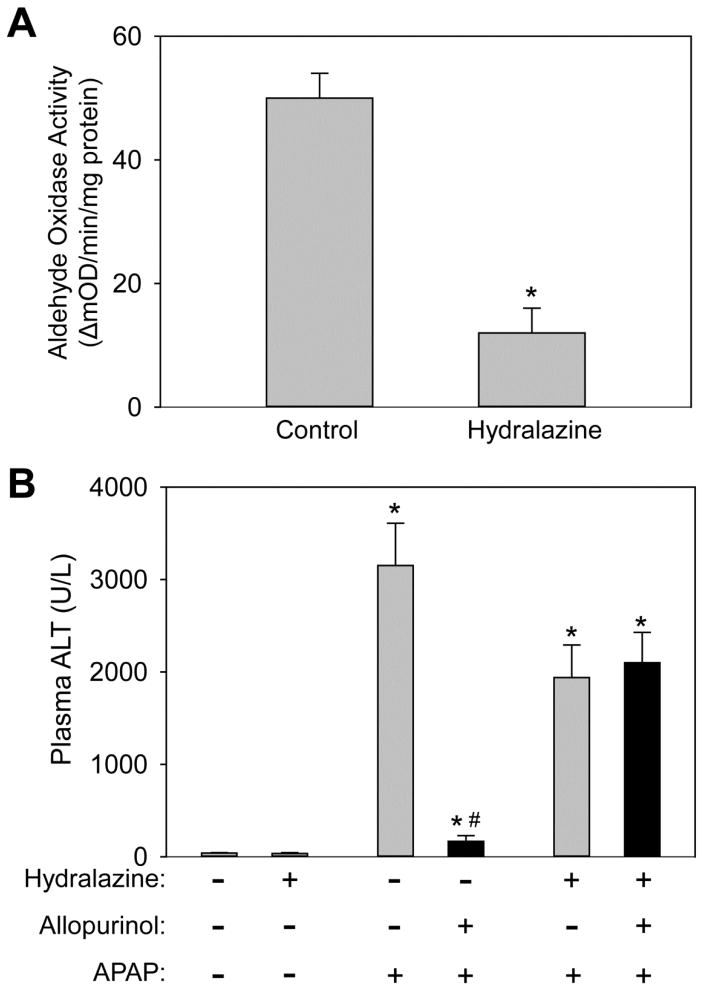
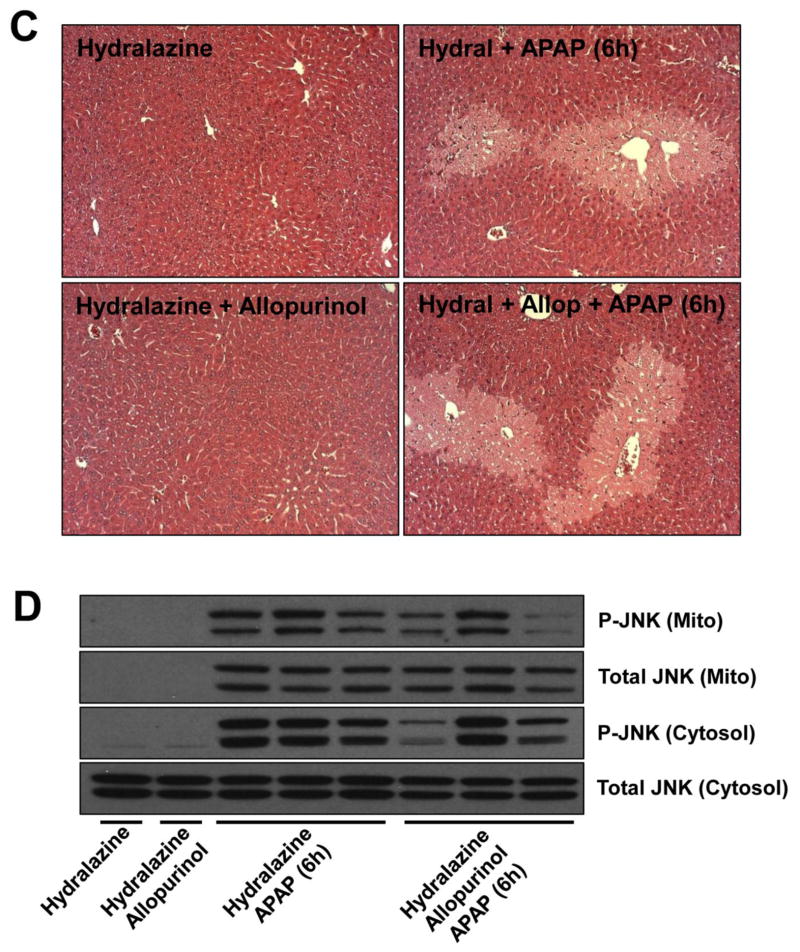
Figure 5. Inhibition of aldehyde oxidase eliminates the protective effect of allopurinol.
To inhibit aldehyde oxidase mice were given drinking water containing hydralazine (0.1 mg/mL) for seven days. On the seventh day mice were given allopurinol or vehicle (18h), fasted overnight and then treated with APAP the following morning for 6h. To verify the hydralazine treatment inhibited aldehyde oxidase liver homogenate was assayed using a spectrophotometric assay with DMAC substrate (A). Plasma ALT of mice pretreated with allopurinol was not different than APAP alone (B). Confirming these data the area of necrosis was not different between these groups (C). The JNK phosphorylation and mitochondrial translocation was evaluated by western blotting (D). Data are expressed as means ± SE, n = 6–10 mice per group. *P<0.05 (compared to control). #P<0.05 (compared to APAP-only, hydralazine with APAP, and hydralazine with APAP with allopurinol).