Abstract
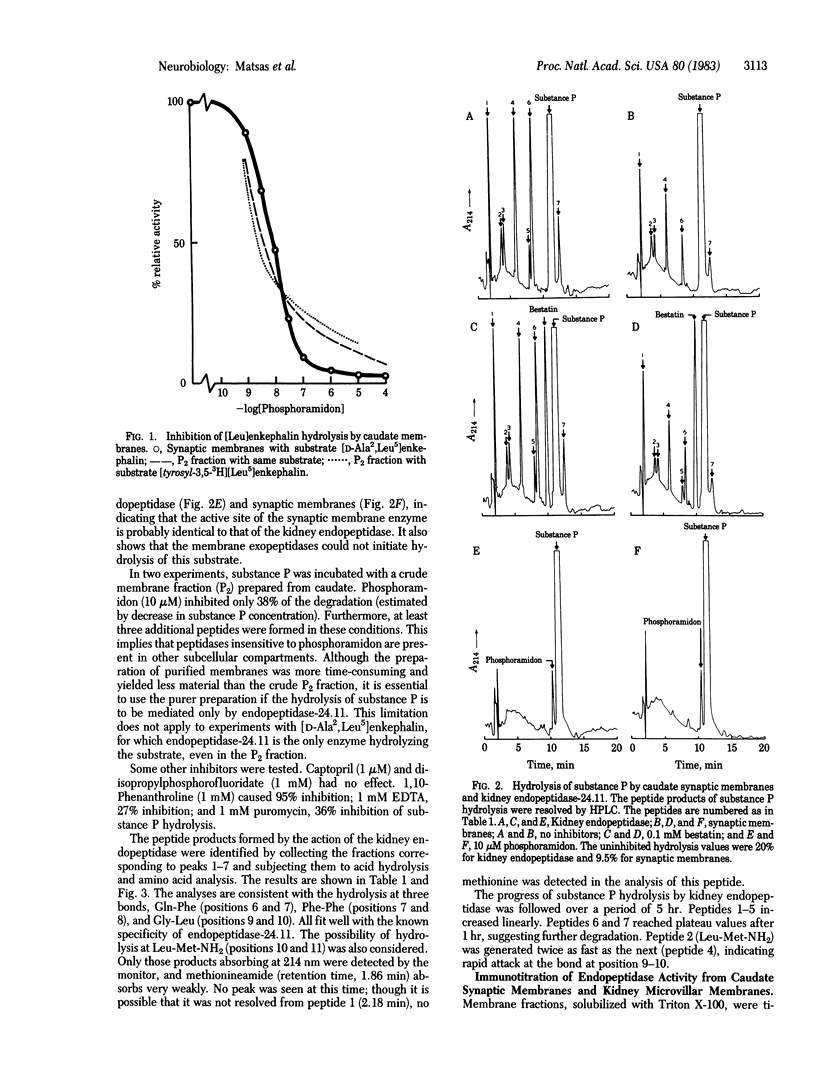
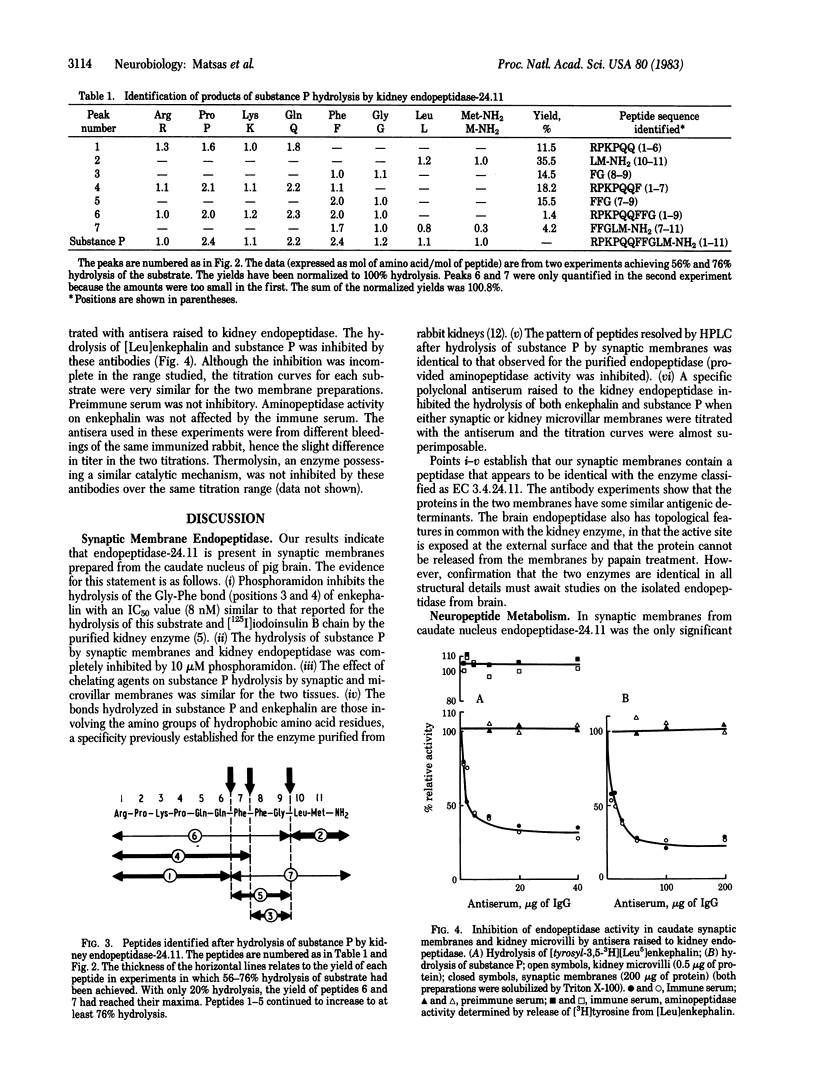
The hydrolysis of [Leu]enkephalin and substance P by purified pig kidney endopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11) and synaptic membranes prepared from pig caudate nuclei has been compared. The hydrolysis of an enkephalin analogue (Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-Leu) at the Gly-Phe bond was completely inhibited by phosphoramidon. The IC50 concentration (8 nM) was similar to that reported for [Leu]enkephalin hydrolysis by the purified endopeptidase [Fulcher, I. S., Matsas, R., Turner, A. J. & Kenny, A. J. (1982) Biochem. J. 203, 519-522]. Seven peptides were produced when substance P (Arg-Pro-Lys-Pro-Gln-Gln-Phe-Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2) was hydrolyzed by the kidney endopeptidase. These were formed by cleavage at bonds Gln-Phe (positions 6 and 7), Phe-Phe (positions 7 and 8), and Gly-Leu (positions 9 and 10). Synaptic membranes generated peptides with the same HPLC retention times and hydrolysis of substance P by either preparation was inhibited completely by 10 microM phosphoramidon. The most susceptible bond appeared to be Gly-Leu (positions 9 and 10). A specific polyclonal antibody raised in rabbits to purified pig endopeptidase inhibited the hydrolysis of [Leu]enkephalin and substance P by detergent-solubilized kidney microvilli or synaptic membranes; the titration curves were essentially identical. We conclude that the endopeptidase, which we suggest should be designated "endopeptidase-24.11," is present in caudate synaptic membranes and could play an important role in the hydrolysis of neuropeptides.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth A., Schulz H., Neubert K. Untersuchungen zur Reinigung und Charakterisierung der Dipeptidylaminopeptidase IV. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1974;32(2-3):157–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benuck M., Grynbaum A., Marks N. Breakdown of somatostatin and substance P by cathepsin D purified from calf brain by affinity chromatography. Brain Res. 1978 Mar 17;143(1):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90764-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen E. M., Vyas J. P., Kenny A. J. A neutral endopeptidase in the microvillar membrane of pig intestine. Partial purification and properties. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):645–648. doi: 10.1042/bj1910645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Kidney neutral endopeptidase and the hydrolysis of enkephalin by synaptic membranes show similar sensitivity to inhibitors. Biochem J. 1982 May 1;203(2):519–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2030519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein C., Snyder S. H. Two distinct enkephalinases: solubilization, partial purification and separation from angiotensin converting enzyme. Life Sci. 1979 Dec 10;25(24-25):2065–2070. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Jessell T., Kanazawa I. Release and metabolism of substance P in rat hypothalamus. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):81–83. doi: 10.1038/264081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Booth A. G., George S. G., Ingram J., Kershaw D., Wood E. J., Young A. R. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, a kidney brush-border serine peptidase. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):169–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1570169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Fulcher I. S. Microvillar endopeptidase, an enzyme with special topological features and a wide distribution. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;95:12–33. doi: 10.1002/9780470720769.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The purification and specificity of a neutral endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):477–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1370477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane A. C., Rance M. J., Walter D. S. Subcellular localisation of leucine-enkephalin-hydrolysing activity in rat brain. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):75–76. doi: 10.1038/269075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Arregui A., Iversen L. L. Substance P degradation by rat brain peptidases: inhibition by SQ 20881. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979;28(4):553–556. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Sandberg B. E., Hanley M. R., Iversen L. L. Purification and characterisation of a membrane-bound substance-P-degrading enzyme from human brain. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):315–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnair D. C., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The amphipathic form of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Biochem J. 1979 May 1;179(2):379–395. doi: 10.1042/bj1790379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Swerts J. P., Guyon A., Roques B. P., Schwartz J. C. High-affinity enkephalin-degrading peptidase in brain is increased after morphine. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):523–526. doi: 10.1038/276523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRorie R. A., Turner R. B., Bradford M. M., Williams W. L. Acrolysin, the aminoproteinase catalyzing the initial conversion of proacrosin to acrosin in mammalian fertilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 26;71(2):492–498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford R. A., Strauss A. W., Powers J. C., Pierzchala P. A., Nishino N., Zimmerman M. A zinc metalloendopeptidase associated with dog pancreatic membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2227–2230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Wilk S. Purification and specificity of a membrane-bound metalloendopeptidase from bovine pituitaries. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4942–4950. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Pert A., Chang J. K., Fong B. T. (D-Ala2)-Met-enkephalinamide: a potent, long-lasting synthetic pentapeptide analgesic. Science. 1976 Oct 15;194(4262):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.968485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Soroca E., Lecomte J. M., Malfroy B., Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. The enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan shows antinociceptive activity in mice. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):286–288. doi: 10.1038/288286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


