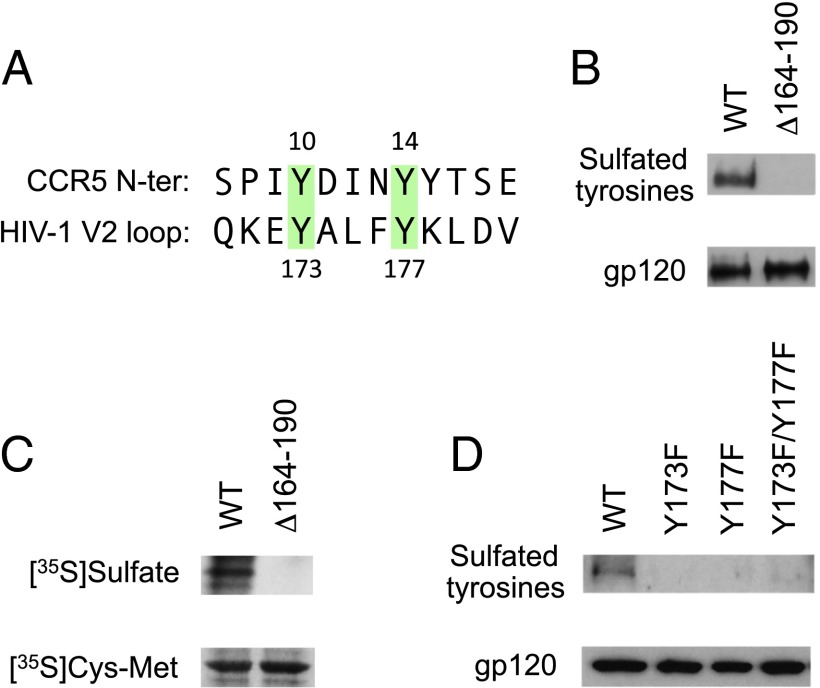
Fig. 1.
The V2 domain of HIV-1 gp120 contains sulfated tyrosines. (A) Sequence alignment of the CCR5 N-terminal domain and the conserved central region of the V2 domain of HIV-1 gp120 (consensus sequence for subtype B). Two colinear conserved tyrosine residues present in CCR5 and gp120 V2 are highlighted in green. (B) Detection of sulfated tyrosines by Western blot in gp120 purified from HeLa cells expressing WT HIV-1 BaL gp160 or a partially V2-deleted mutant (Δ164–190) lacking Tyr173 and Tyr177 by vaccinia technology. gp120 was immunoprecipitated from the cell surface and analyzed by Western blot using a specific mAb for sulfated tyrosines (1C-A2); a murine anti-gp120 mAb (b13) was tested in parallel as a loading control (gp120). (C) Detection of sulfated tyrosines by autoradiography in metabolically labeled HEK293 cells expressing HIV-1 BaL WT or Δ164–190 gp160 by vaccinia technology. The cells were labeled with free [35S]sulfate or [35S]cysteine/[35S]methionine by overnight culture in sulfate-free or cysteine/methionine-free medium, respectively. The films were exposed for 48 h for [35S]sulfate labeling and for 18 h for [35S]cysteine/[35S]methionine labeling. (D) Detection of sulfated tyrosines by Western blot in HEK293 cells transfected with a plasmid encoding WT HIV-1 BaL gp160 or the phenylalanine-substituted mutants BaL Y173F, BaL Y177F, and BaL Y173F/Y177F. Western blot analysis was performed as in B.