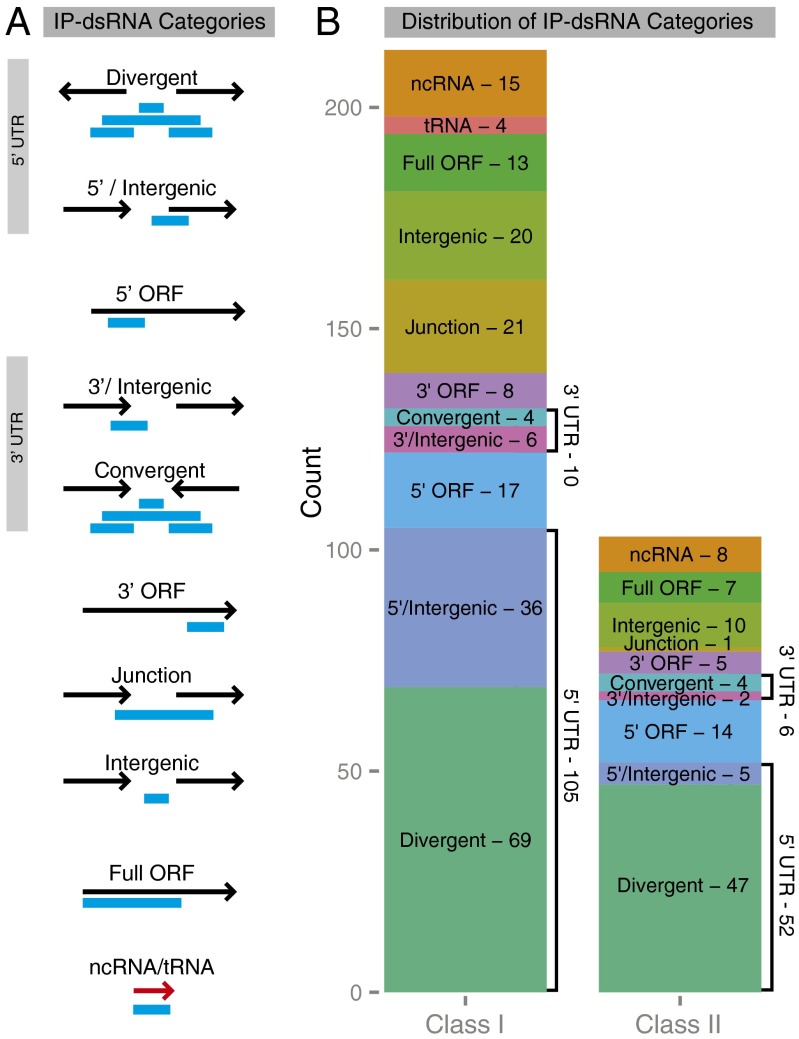
Fig. 3.
Genomic location of the dsRNAs. The IP-dsRNAs were categorized based on their location relative to annotated ORFs in that region of the genome (EcoCyc). (A) Schematic illustration of the categories of IP-dsRNAs. IP-dsRNAs identified at the 5′ end of genes in a divergent orientation were classified as divergent, whereas those at the 3′ ends of convergent genes were classified as convergent. IP-dsRNAs near head-to-tail-oriented genes were classified as gene junction if spanning the 3′ end of the upstream gene and the 5′ end of the downstream gene, as intergenic if located between the two genes, or 5′/intergenic or 3′/intergenic if spanning one gene boundary, but not both gene boundaries. If they covered more than one-half of an ORF, they were classified as full ORF. If they were contained in the 3′ or 5′ half of an ORF, they were classified as 3′ or 5′ ORF, respectively. (B) Bar graph summarizing the distribution of the IP-dsRNA categories.