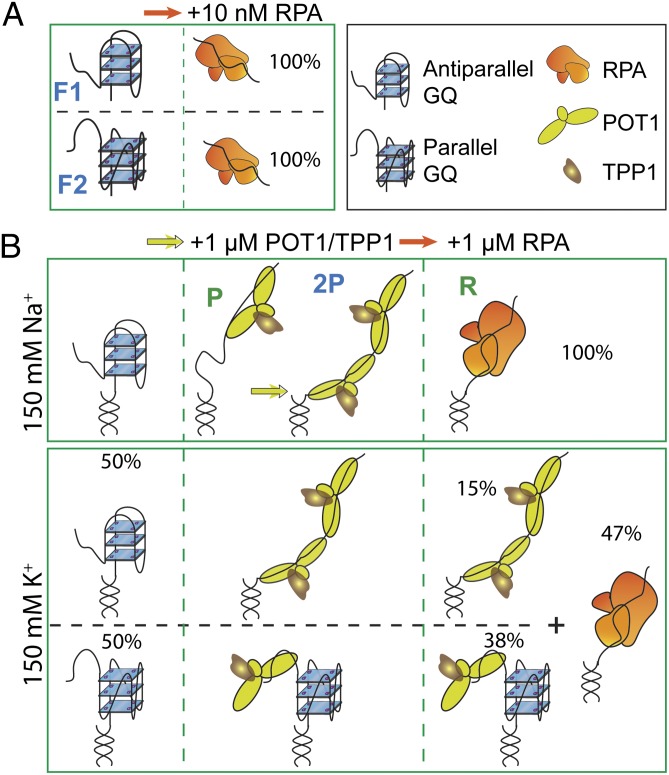
Fig. 6.
A model for protection of ssTEL4 against RPA-mediated unfolding. (A) In the absence of POT1/TPP1, RPA unfolds both antiparallel (F1) and parallel (F2) conformations at a low concentration either in Na+ or in K+. (B) In 150 mM Na+, ssTEL4 forms only antiparallel GQ. Binding of one (P) or two (2P) POT1 unfolds the antiparallel conformation. Addition of RPA displaces POT1/TPP1 from ssTEL4. In 150 mM K+, POT1/TPP1 binds to both GQ folding patterns and unfolds antiparallel GQ, whereas parallel GQ remains folded. Binding of two POT1s to ssTEL4 is required to stabilize the unfolded state. POT1/TPP1 binding effectively suppresses RPA binding to ssTEL4 even at high RPA concentrations. In particular, the majority of parallel GQ remains stably folded against RPA-mediated unfolding.