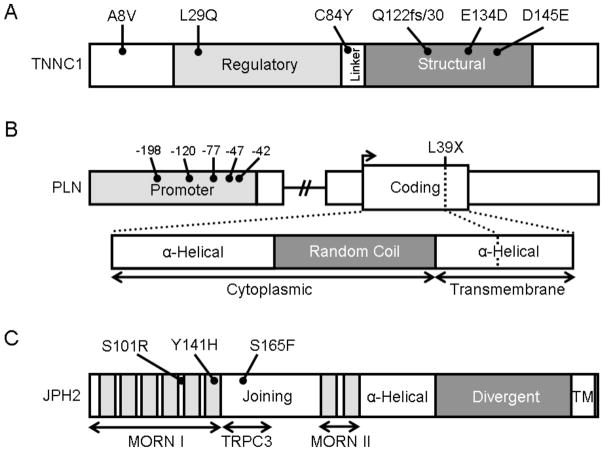
Fig. (2). Protein topology with all HCM-associated mutations for TNNC1, PLN, and JPH2.
A. Linear topology of the 6 exon-encoded, 161 amino acid TNNC1. Domains include the regulatory EF-hand (light gray), the linker, and the structural EF-hand domain (dark gray). B. Schematic of the proximal promoter (light gray), coding sequence, and protein topology of the 1 exon-encoded, 52 amino acid PLN. Domains of PLN include two α-helical domains separated by random coil (dark gray). The amino-terminal aspect of the protein is cytoplasmic while the carboxy-terminus is a hydrophobic, SR-associated domain. C. Linear topology of the 5 exon-encoded, 696 amino acid JPH2. Domains include the MORN I and II domains which each contain multiple MORN motifs (light gray) and are separated by the joining region domain. Contained within the joining region is the TRPC3 reciprocal binding domain identified in rodent models of skeletal muscle. A putative α-helical domain connects the MORN II domain with the divergent domain (dark gray) and a carboxy-terminal transmembrane domain (TM) associates with the SR.