Fig. 1.
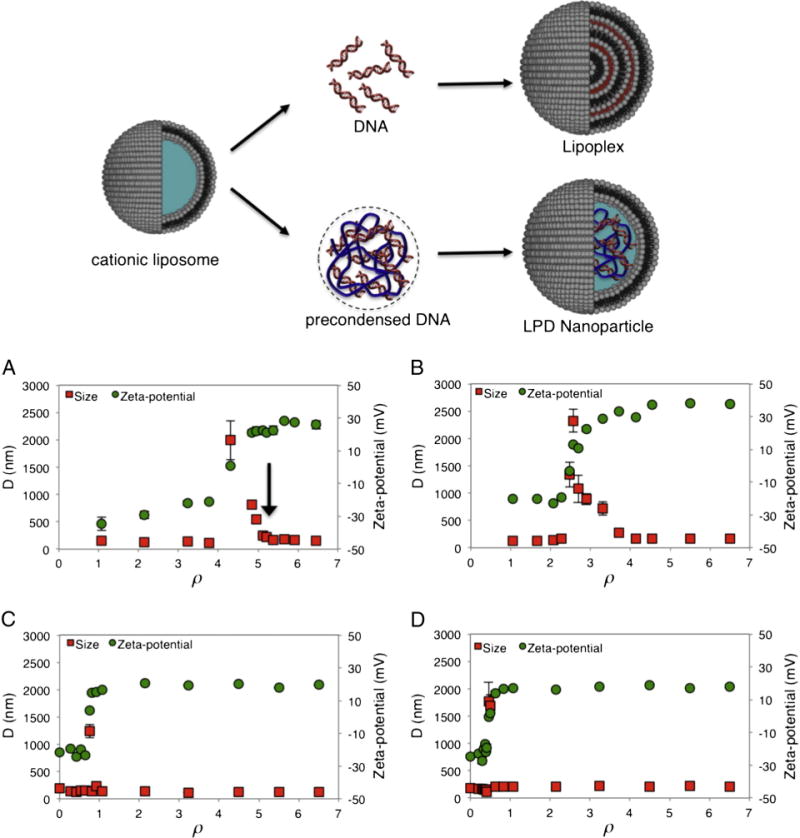
(Cartoon) Mechanism of formation of lipoplexes and lipid nanoparticles: lipoplexes are typically formed by bulk mixing between cationic liposomes and DNA solutions and are arranged as multilayer structures in which DNA is intercalated between alternating lipid bilayers. Lipid NPs are composed of a core of DNA complexed with protamine and covered by a lipid shell that protects DNA from degradation, imparts biocompatibility and improves stability in biological fluids. The hydrodynamic radius, D, and the zeta-potential of DOTAP–DOPC/DNA (panel A), DC-Chol–DOPE/DNA (panel B) lipoplexes and DOTAP–DOPC/P-DNA (panel C), DC-Chol–DOPE/P-DNA (panel D) nanoparticles, as a function of the cationic lipid/DNA charge ratio, ρ.
