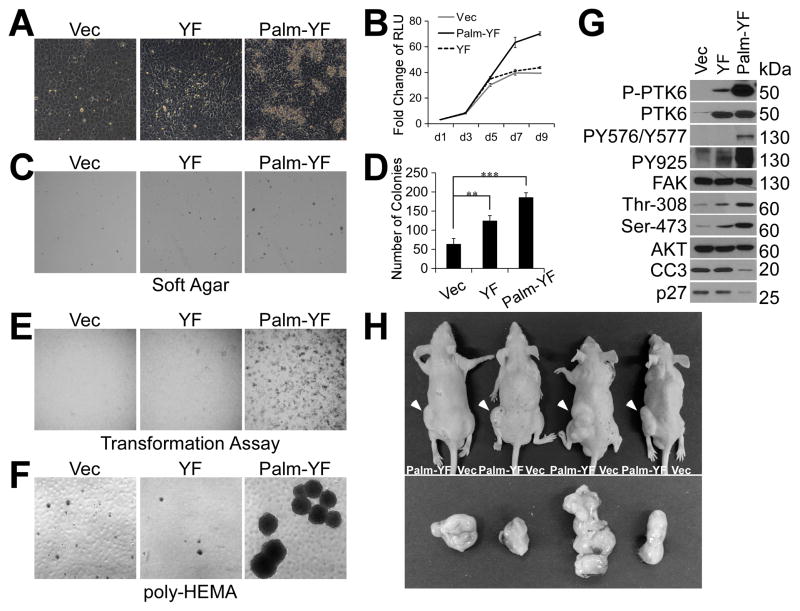
Figure 3. Membrane associated active PTK6 transforms SYF MEFs.
A. SYF cells stably expressing Palm-PTK6-YF are able to overcome contact inhibition. SYF cells stably expressing vector, PTK6-YF or Palm-PTK6-YF were seeded at complete growth medium, and images were taken 5 days after confluence. B. Growth curve of SYF cells as measured by CellTiter-Glo luminescent cell viability assay demonstrates the ability of Palm-PTK6-YF expressing cells to continue growing after confluence. Y axis is the fold change of relative luminescence unit (RLU), with day 1 set to 1. C. SYF cells expressing PTK6-YF or Palm-PTK6-YF show increased anchorage independent growth in soft agar assay. D. A bar graph illustrates the number of colonies formed inn soft agar assay in C (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001). E. Transformation (foci-forming) assays show increased foci-forming ability of SYF cells expressing Palm-PTK6-YF. F. Palm-PTK6-YF expressing SYF cells are able to proliferate under suspended growth conditions. Anoikis assays were performed on poly-HEMA coated plates for 6 days. G. Palm-PTK6-YF activates FAK and AKT survival signaling pathways. Palm-PTK6-YF expressing SYF cells were seeded on poly-HEMA coated plates for 72 hours. Immunoblotting analysis was performed with anti-P-PTK6 (Tyr342), PTK6, P-FAK (Tyr576/Tyr577), P-FAK (Tyr925), FAK, P-AKT (Thr308), P-AKT (Ser473), AKT, cleaved caspase 3 (CC3) and p27 antibodies. H. SYF cells expressing Palm-PTK6-YF form tumors in xenograft mice. Palm-PTK6-YF expressing cells were injected subcutaneously in left flanks of nude mice, and control cells were injected in right flanks. Tumors were indicated by white arrows. Mice were sacrificed 4 weeks after injection, and tumors were taken out for further analysis.