Fig. 2. Curcumin and 5-Aza augment miR-203 expression in T24 bladder cancer cell line.
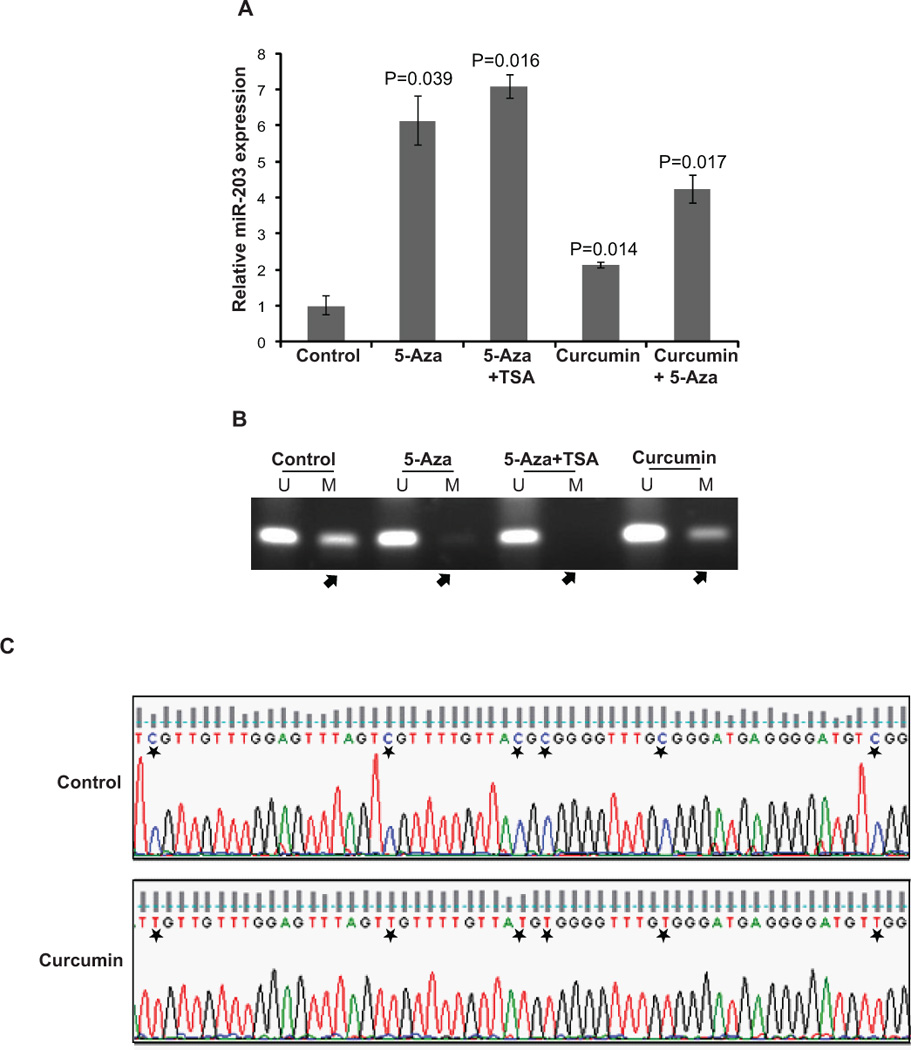
To examine the potential modulation of miR-203 by epigenetic drugs, T24 cells were treated with various epigenetic dugs either singly or in combination. Treatments included vehicle control (C) or 5-Aza (5 µM), 5-Aza (5 µM) +TSA (100ng), curcumin (10 µM), curcumin (10 µM) + 5-Aza (5 µM).
(A) Relative miR-203 expression was assessed after the various treatments by RT-PCR. Curcumin and 5-Aza alone or in combination significantly upregulated miR-203 expression.
(B) MS-PCR analysis of the human miR-203 upstream region following various treatments. Curcumin and 5-Aza treatment leads to partial demethylation of the miR-203 promoter (indicated by arrows). The corresponding full length electrophoretic gel for this section is shown in Fig. S3.
(C) Bisulfite DNA sequencing for miR-203 promoter following curcumin/control treatment. Curcumin treatment leads to demethylation of CpG sites in miR-203 promoter as indicated by asterisks.
