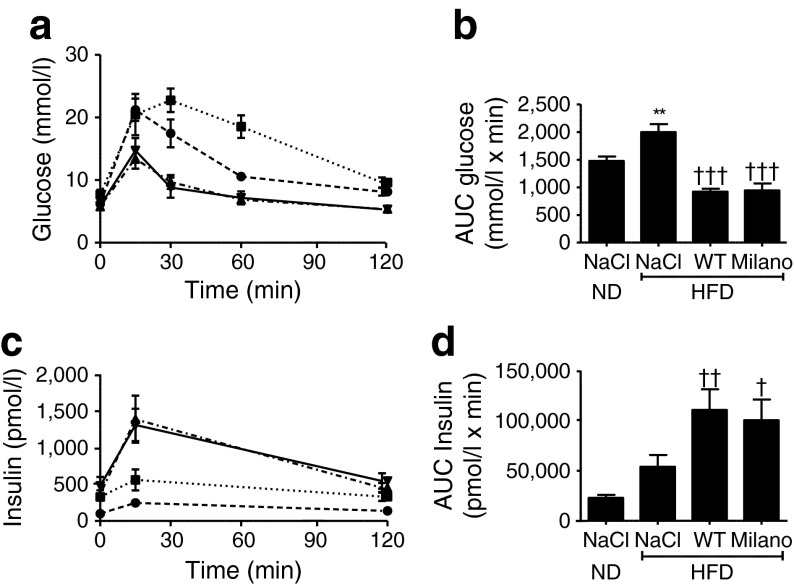
Fig. 2.
Acute apoA-I treatment improves glucose-disposal capacity in GTTs. ND and HFD mice were treated for 3 h with a single injection (14 mg/kg body weight) of apoA-I WT (triangles/dash-dot line in HFD), apoA-I Milano (upside down triangles/solid line in HFD) or NaCl (circles/dashed line in ND; squares/dotted line in HFD). Mice received an i.p. glucose load (50 mg/mouse) 3 h after injection of NaCl, apoA-I or apoA-I Milano followed by determination of (a) glucose and (b) insulin concentration at the indicated time points. (c) and (d) show the AUC values of glucose and insulin levels, respectively, during the GTT. n = 6–8; **p < 0.01 for NaCl HFD control vs NaCl ND control; † p < 0.05, †† p < 0.01, ††† p < 0.001 for apoA-I (WT or Milano) vs NaCl HFD control