Figure 7.
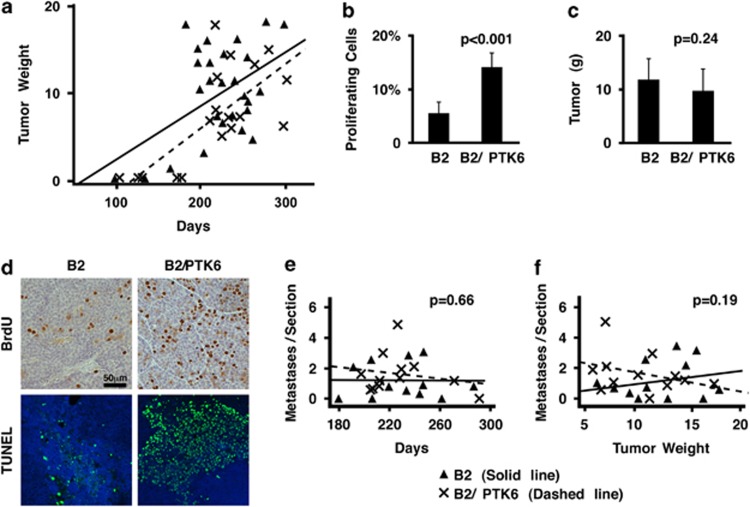
Transgenic expression of PTK6 in the MMTV-ERBB2 mouse model does not enhance ERBB2-driven tumorigenesis (a) Mammary gland tumors from ERBB2 (B2; n=28) and ERBB2/PTK6 mice (B2/PTK6; n=18) were harvested and analyzed at various time points; total tumor weight is plotted against age (days; see key below 7e and f). Tumor occurrence between ERBB2 and ERBB2/PTK6 animals did not show a statistically significant difference (P=0.70). However, regression analysis suggested a delay in tumor initiation in ERBB2/PTK6 animals (P<0.001). (b) Proliferation in tumors that developed in ERBB2 (B2; n=10) and ERBB2/PTK6 (B2/PTK6; n=10) transgenic mice was examined using BrdU labeling. ERBB2/PTK6 tumors exhibited higher levels of proliferation than ERBB2 tumors, even in tumors of the same size. The number of BrdU-labeled epithelial cells in ERBB2/PTK6 tumors is three fold higher than in ERBB2 tumors (P<0.001), but the tumor size between these two groups is not significantly different (P=0.24) (c). (d) Although ERBB2/PTK6 tumors display higher levels of proliferation (BrdU incorporation), they also exhibit increased apoptosis. Increased apoptosis is detected in tumors that formed in ERBB2/PTK6 double transgenic animals compared with tumors that formed in ERBB2 transgenic mice. Apoptosis was analyzed using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay in several pairs of equivalently sized ERBB2 and ERBB2/PTK6 tumors. (e, f) We examine lung metastases in single ERBB2 and double ERBB2/PTK6 transgenic mice and correlated the development of metastases with age (e) and primary mammary gland tumor weight (f) are shown. Linear regression models were fitted to the data and Wald tests were conducted to compare regression slopes between the ERBB2 (B2) and ERBB2/PTK6 (B2/PTK6) transgenic groups, resulting in P-values of 0.66 and 0.19 for (e) and (f), respectively, suggesting that the slopes from two experimental groups are not statistically different from each other.