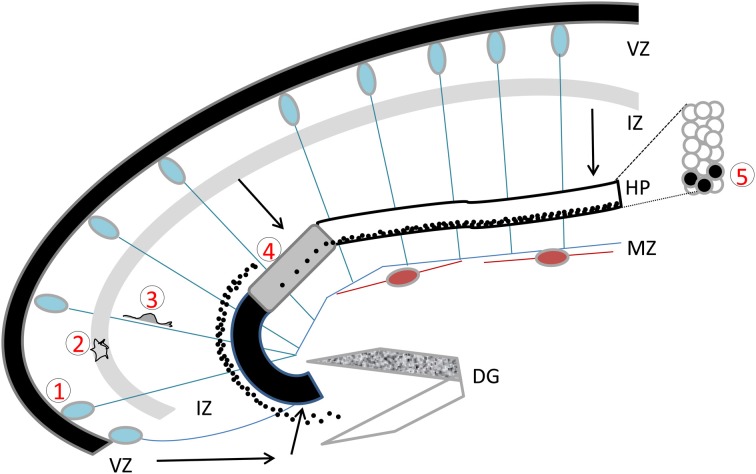
Figure 1.
The developing hippocampus. Radial glial cells are represented with their somata in the ventricular zone (VZ) and long basal processes extending up to the marginal zone (MZ). These processes serve as guides for migration. Cajal Retzius cells are schematized in brown. Migration pathways across the intermediate zone (IZ) are indicated by arrows. The hippocampal plate (HP) is shown in white, gray, and black to indicate the CA1, CA2, and CA3 fields respectively. The dentate gyrus (DG) is indicated as a V-shaped structure, at this stage the inferior blade (shown in white) is not completely formed, whereas the superior blade (shown in mottled gray) is taking shape. A BrdU injection at E18 in the rat, with sacrifice 4 days later reveals BrdU-labeled cells as schematized by the black dots: cells born at E18 have already reached the CA1 developing pyramidal cell layer, whereas CA3 cells are still found in the IZ, requiring another full day to cross the CA3 pyramidal cell layer. An inset shows the organization of somata in the pyramidal cell layer. Five successive steps of development are indicated, (1) cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the VZ; (2) a multipolar phase above the VZ; (3) a bipolar phase of migration through the IZ; (4) insertion in the hippocampal plate; (5) settling in the appropriate layer. Schema based on data shown in Altman and Bayer (1990b), Figure 3.