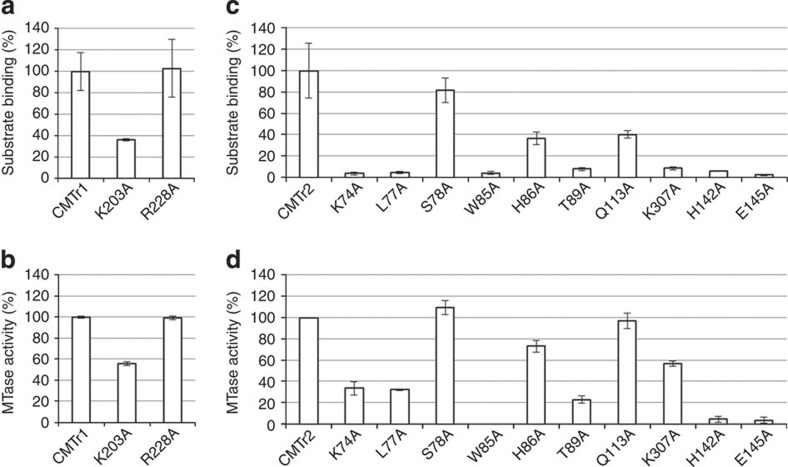
Figure 5. MTase activity and RNA binding by CMTr1 and CMTr2 variants with single-residue substitutions.
The analysis was performed for full-length wild type and single substitution variants of CMTr1 (a,b) and CMTr2 (c,d). (a,c) Effect of single amino-acid substitutions on MTase activity. In vitro transcribed RNA-GG molecules with a 32P-labelled cap0 (a) or cap01 (c) structure were incubated with the indicated enzymes in the presence of SAM. Product RNA was digested with nuclease P1 (a) or RNase T2 (c) and purified by phenol/chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation. The digestion products were resolved on 21% polyacrylamide/8 M urea gel and quantified after autoradiographic visualization. (b,d) Effect of single amino-acid substitutions on substrate binding. In vitro transcribed RNA-GG molecules with a 32P-labelled cap0 (b) or cap01 (d) structure were incubated with the indicated enzymes in the presence of SAH. After 30-min incubation, the samples were filtered through a nitrocellulose membrane and washed with a reaction buffer. RNA bound to membrane-attached proteins was visualized by autoradiography and quantified. The signal from the negative control (the sample with the BAP protein) was subtracted from the signal from samples with cap MTases. The analyses were performed in triplicate. The relative activity/binding compared with the wild type enzyme (set at 100%) and s.d. values are shown.