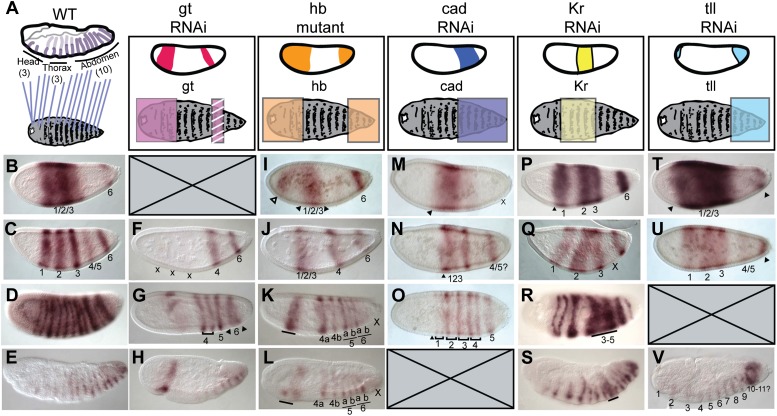
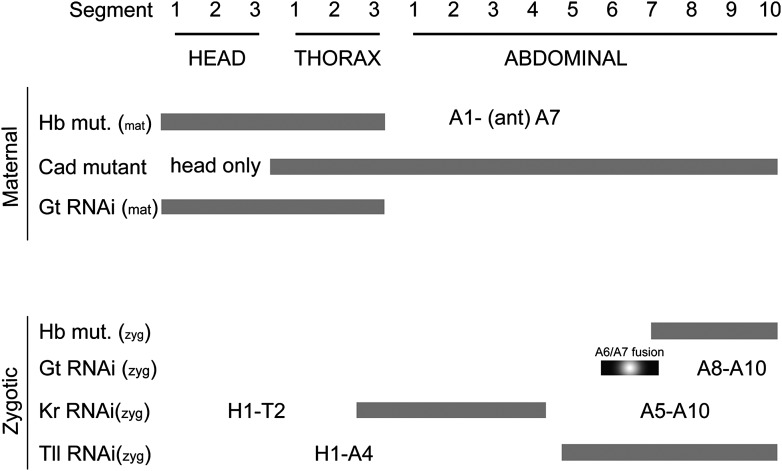
Figure 2. Nv eve epistasis with maternal and gap genes.
(A) Schematic representation of the germ-band-extended embryo, showing 16 single-segment stripes of Nv eve expression, and their segment counterparts in the patterned larval cuticle. Colored boxes cover the segments of the larval cuticle that are lost or fused in each RNAi background. All embryos are shown anterior left, dorsal up (except where indicated). Nv eve mRNA expression is shown in each embryo (B–G). Wild-type (WT) embryos are shown as staged controls for RNAi embryos. (B) WT early blastoderm embryo. (C) WT cellular blastoderm embryo. (D) WT early gastrula extension embryo. (E) WT germ-band-retracted embryo. (F–H) gt RNAi embryos stained for Nv eve mRNA expression. (F) Cellular blastoderm embryo with reduced Nv gt exhibits loss of anterior Nv eve stripes (x). (G) Nv gt RNAi embryo in early germ-band-extension exhibits loss of anterior Nv eve stripes and improper splitting of Nv eve stripe 5, as well as aberrant dorsal anterior expression of Nv eve. (H) Nv gt RNAi embryo at dorsal closure exhibits a stripe of Nv eve at the anterior, as well as a reduced number of posterior segmental Nv eve stripes. (I–L) Nv hb mutant embryos stained for Nv eve mRNA expression. (I) Early blastoderm Nv hb mutant embryos have a reduced central Nv eve domain (bounded by black arrowheads), and an ectopic anterior Nv eve stripe (white arrowhead). (J) Nv hb mutant cellular blastoderm embryo with a single anterior domain of Nv eve that has failed to resolve, and a single stripe 4 which exhibits delayed splitting. (K) Nv Hb mutant germ-band extension embryo with fused anterior domain (line) and 6 segmental stripes, representing derivatives of Nv eve stripes 4 and 5 and two derivatives of stripe 6; additional stripe 6 derivatives are absent (x). (L) hb mutant dorsal closure embryo exhibiting fused anterior domain (line) and the same number of derivatives as in (M), with more posterior segments missing (x). (M–O) Nv cad RNAi embryos stained for Nv eve mRNA expression. (M) Nv cad RNAi early blastoderm with reduced central Nv eve domain that is also posteriorly shifted (anterior boundary indicated by black arrowhead). (N) Nv cad RNAi cellular blastoderm embryo with posteriorly shifted (arrowhead), reduced Nv eve central domain, whose splitting is delayed. (O) Nv cad RNAi early gastrula embryo with posterior shift in Nv eve expression (black arrowhead). Four double-segment periodicity stripes are split into single-segment stripes and stripe 5 remains intact. (P–S) Nv Kr RNAi embryos stained for Nv eve mRNA expression. (P) Nv Kr RNAi precellular blastoderm embryo with aberrant Nv eve central domain resolution, where stripes 2–3 appear posteriorly shifted. (Q) Dorsolateral view of a Nv Kr RNAi embryo where stripes 2 and 3 are less refined than WT and 3 is posteriorly shifted. No stripe 4/5 expression is detected (X). (R) Nv Kr RNAi early gastrula embryo with aberrant stripe 2 splitting and aberrant resolution of stripes 3–5. (S) Moderately affected Nv Kr RNAi germ-band retraction embryo with fused segments in the middle of the embryo (line). (T–V) Nv tll RNAi embryos stained for Nv eve mRNA expression. (T) Nv tll RNAi early blastoderm embryo with expanded Nv eve expression domains toward both poles (arrowheads). (U) Nv tll RNAi precellular blastoderm embryo showing delayed resolution of Nv eve stripes 1–3 and Nv eve stripe 6 shifted to the extreme posterior pole of the embryo (arrowhead). (V) Nv tll RNAi dorsal closure embryo showing abnormal posterior Nv eve stripe formation.
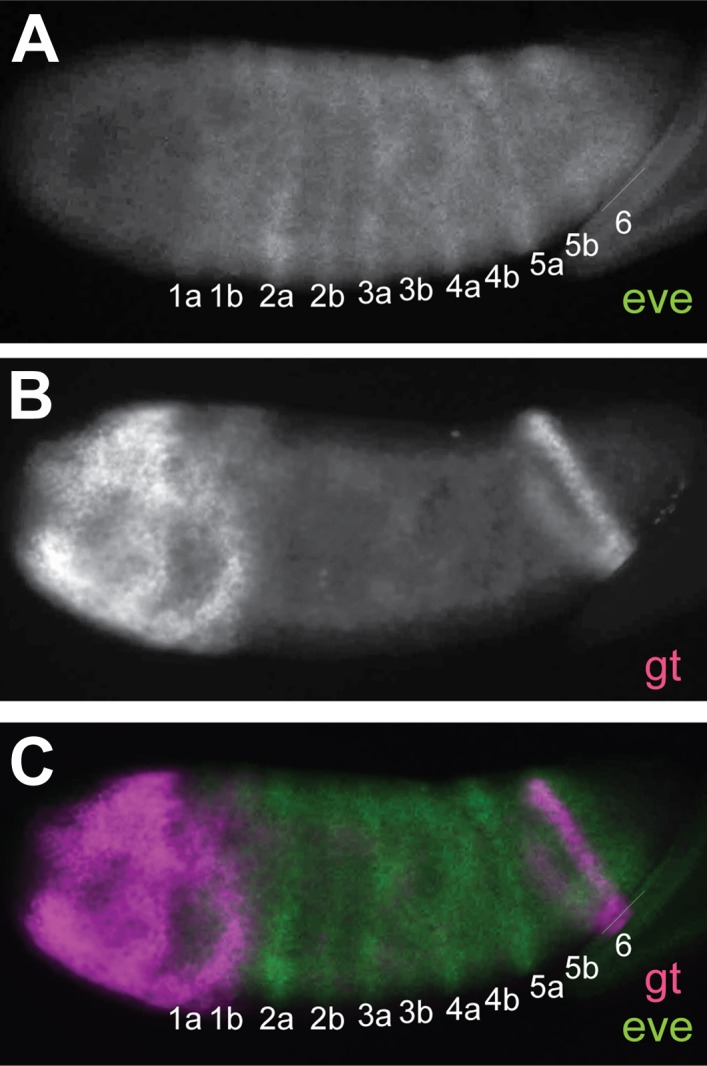
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Nv eve/Nv gt double FISH in the embryo.