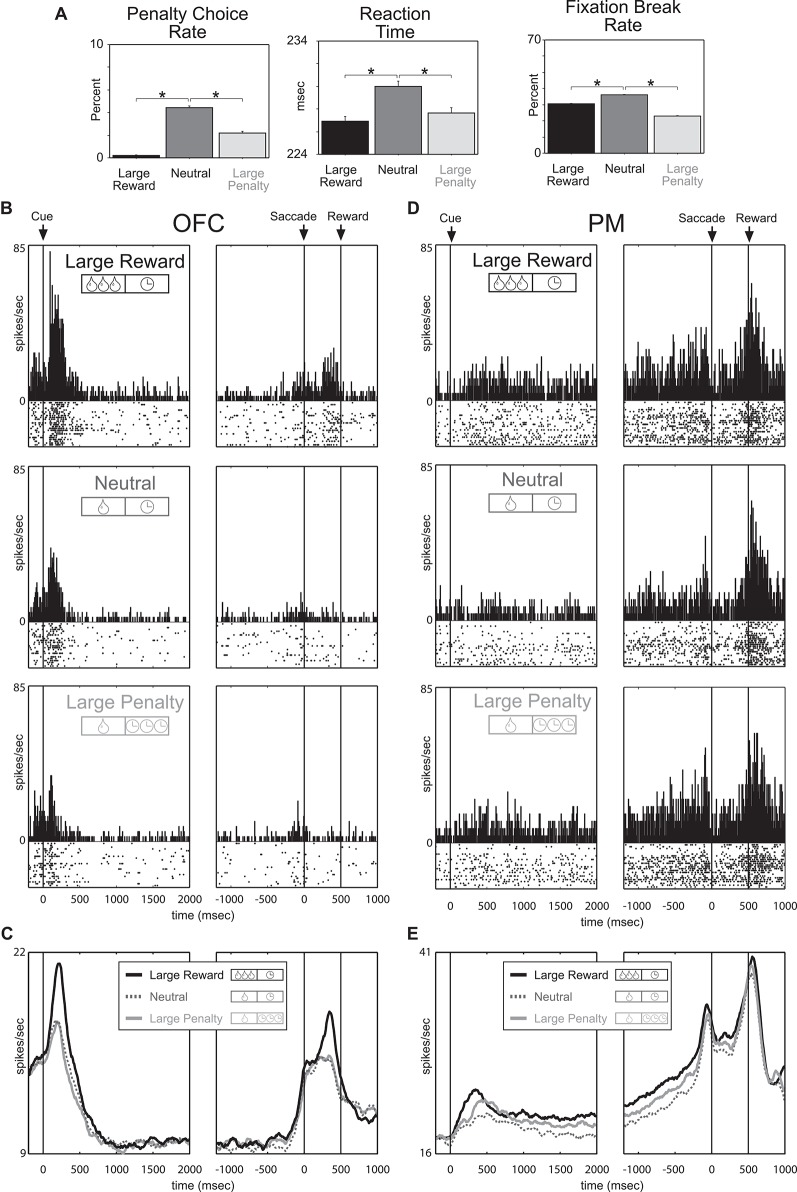
Figure 2.
Premotor and Orbitofrontal cortex encode motivation and value, respectively. Trials fell into three categories defined by reward-penalty combination: large reward (large reward and small penalty), neutral (small reward and small penalty), and large penalty (small reward and large penalty). (A) Performance measures sensitive to reward and penalty size. Penalty choice rate: trials on which the monkeys chose penalty expressed as a fraction of all trials on which they chose reward or penalty. Fixation break rate: trials terminated by a fixation break expressed as a percentage of all trials. Reaction time: average interval between fixation spot offset and saccade initiation on all trials in which the monkey made a saccade in the rewarded direction. Asterisks (all planned comparisons): statistically significant differences at P < 0.001. (B, C) Neuronal activity in OFC reflects the value conveyed by the incentive cues. (B) Shown are data from a single neuron firing during the cue period at a rate that was especially high for large reward and especially low for large penalty. (C) Mean firing rate as a function of time under the three incentive conditions for all 176 OFC neurons. (D, E) Neuronal activity in premotor (PM) reflects the motivational impact of the incentive cues. (D) Shown are data from a single neuron firing throughout the trial at a rate that was high for large reward and large penalty. (E) Mean firing rate as a function of time under the three incentive conditions for all 135 PM neurons. Adapted from Roesch and Olson (2004).