Figure 1.
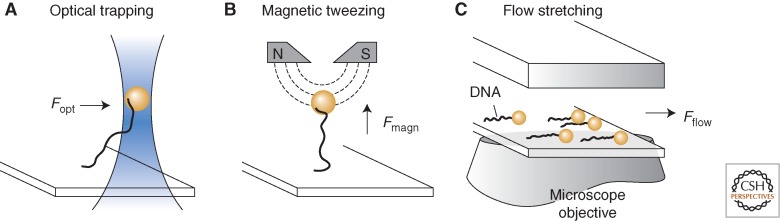
DNA stretching techniques. Three methods of DNA nanomanipulation are shown. (A) Optical trapping: A focused beam of light traps a bead that is tethered to DNA. Feedback control allows the position and force on the bead to be precisely monitored and controlled. (B) Magnetic tweezing: Permanent magnets located above the sample generate a vertical extending force on DNA through a magnetic bead. (C) Flow stretching: DNA-tethered beads are extended using laminar flow and imaged using wide-field optical microscopy. In all cases, the end of the DNA opposite the beads is attached to a functionalized glass surface.
