Fig. 2.
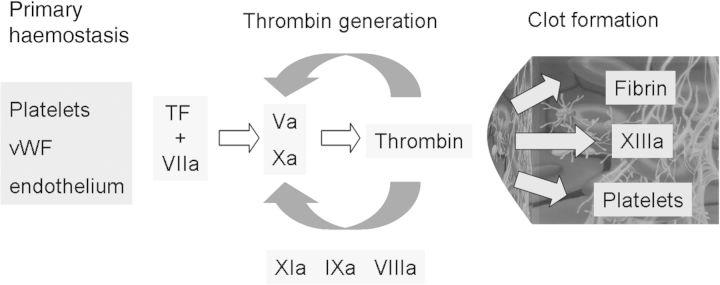
Three phases of coagulation from an analytical point of view. (i) Primary haemostasis: based on an interaction of platelets, vWF and endothelium. (ii) Thrombin generation: induced by tissue factor (TF) and Factor VIIa. The TF–VIIa complex activates the conversion of Factor X to Factor Xa and leads to the production of a small amount of thrombin. Thrombin is amplified by activation of intrinsic coagulation factors (VIIIa, IXa, XIa) and Factor V. The thrombin burst results in clot formation. (iii) Clot formation: the clot is formed by fibrin and activated PLTs and stabilized by Factor XIIIa. All three components are activated by thrombin, which is the key enzyme for clot formation.
