Figure 6. Unlike alloantigen-stimulated naïve CD8+ cells, CD8regs lack cytotoxic activity against allogeneic T cells.
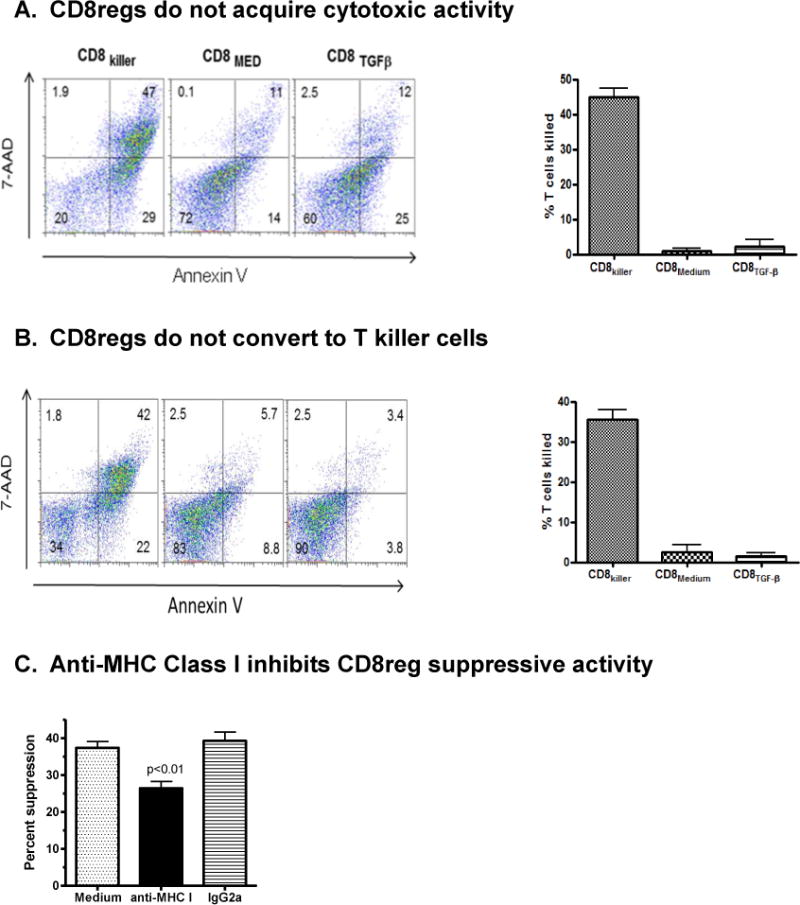
A. Naïve CD8 cells were cultured ratio for 7 days with CD3/CD28 beads, IL-2 and with or without TGF-β to generate CD8regs. CD8 killer cells were generated by culturing CD8 cells with allogeneic mature dendritic cells at a 30:1 T cell:DC ratio. Each CD8 cell subset was then mixed with CFSE-labeled concanavalin activated T cells from the DC donor for 4 hours, at a 30:1 effector to target cell ratio. Killing of target cells defined by CFSE-labeled cells double stained for Annexin V and 7-AAD was then determined by flow cytometry. Shown is representative example. Scatter plots showing the characteristics of the controls used is shown in Supplementary Fig. 1. The bar graph indicates the mean and SEM of specific killing for each CD8 subset of the four healthy donors studied. This was calculated using the formula given in Methods. P values, <0.001, compared CD8killer with each CD8reg subset.
B. To determine whether CD8regs can be converted into cytotoxic killer cells by allogeneic stimulation, CD8regs were harvested at day 7, then co-cultured with irradiated allogeneic non-T cells for 6 days or DCs and examined for cytotoxity as described above. A representative example of Annexin V and 7AAD staining from one of three healthy donors studied and a summary of the calculated CTL activity of the three donors is shown in the bar graph. In these experiments the positive controls were CD8 cells stimulated with allogeneic non-T cells for 6 days. The flow cytometry data for baseline and maximal annexin V and 7AAD staining is shown in supplemental Fig. 1.
C. To confirm that that CD8regs could recognize foreign alloantigens expressed by the target CD4 cells, anti-human HLA A,B,C or isotype control IgG2a (10mg/ml) was added to the in vitro suppressor assay using the protocol described in Fig. 4A. The bar graph shows the mean ± SEM suppressive activity of three donors. Anti-HLA class I antibodies significantly decreased suppressive activity compared with control IgG (p.<0.01).
