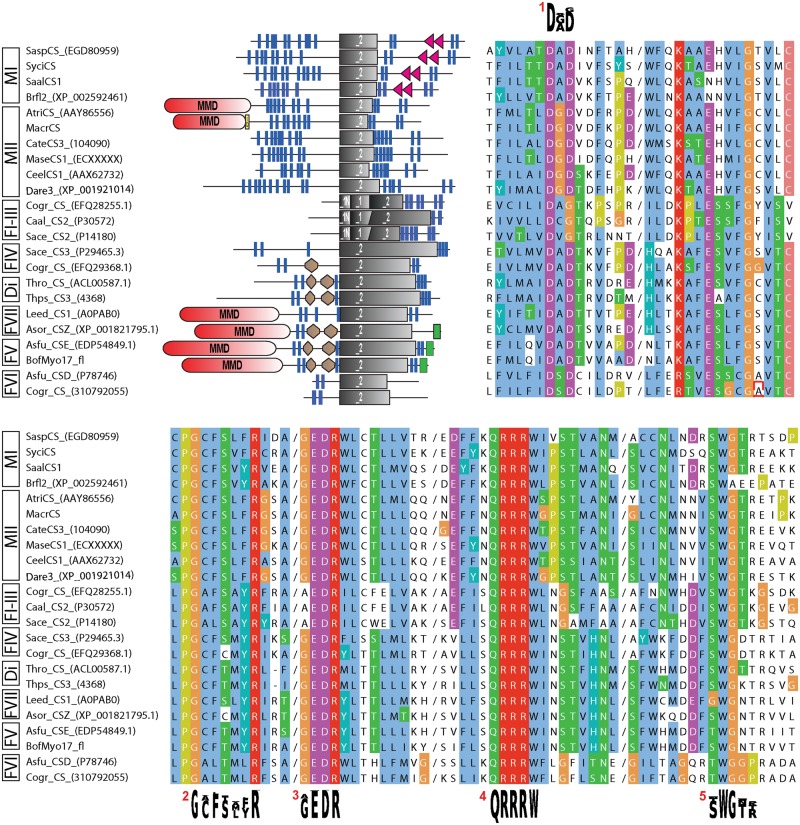
Fig. 1.—
Overview of protein domain architecture and sequence characteristics of a subsample of the analyzed CSs. Clipped alignment (clustalx coloring; cuts indicated by a slash) showing conserved glycosyltransferase family 2 and CS motifs (consensus sequence shown as sequence logos). 1/2, donor saccharide binding; 3, acceptor saccharide binding; 4, product binding; 5, CS-specific motif (possibly involved in chitin translocation). Brown hexagon, Cyt-b5 (Cytochrome b5-like heme/steroid-binding domain); gray rectangle, Pfam CS domains (_1N: Chitin_synth_1N, _1: Chitin_synth_1, _2: Chitin_synth_2); green rectangle, C terminal domain of chromatin-associated protein DEK; MMD (red), myosin motor domain; red triangle, SAM domain; yellow box, IQ domain. Di, diaotome CSs; F1-VII, fungal CSs classes I–VII; MI/C, metazoan type I and choanoflagellate CSs; MII, metazoan type II CSs. For abbreviations of species and protein references, see supplementary table S2, Supplementary Material online.