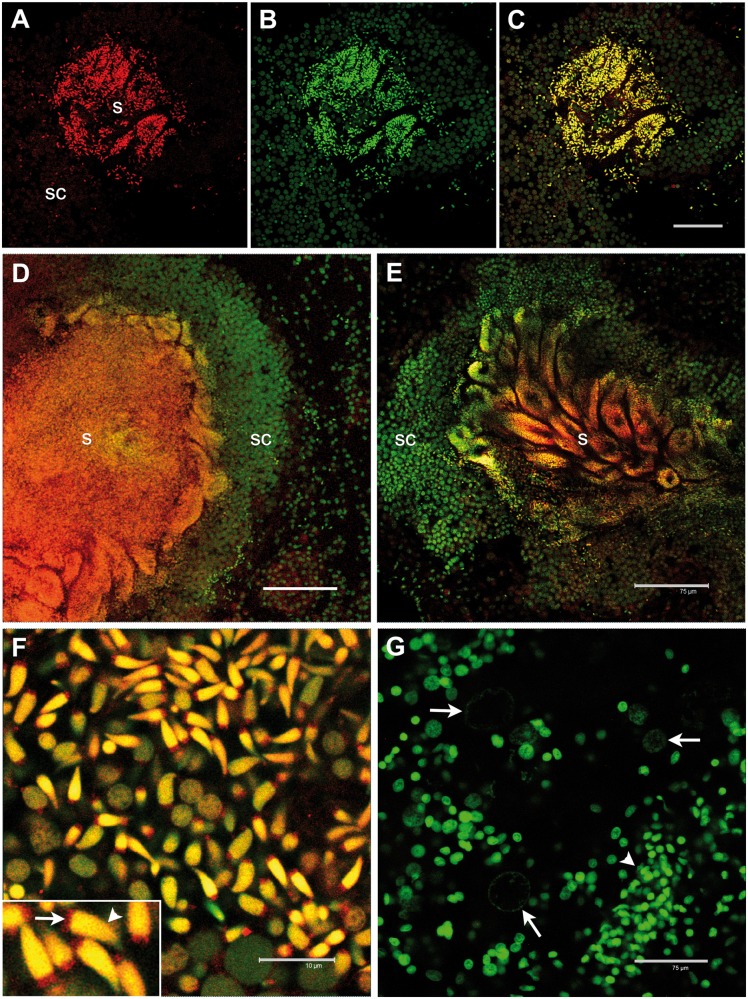
Fig. 3.—
RPHM21 protein localization in Ruditapes philippinarum testis. (A) RPHM21 antibody staining (in red) on a whole male acinus section (s: mature spermatozoa; sc: spermatogenic cells); (B) the same section stained with the nuclear dye TO-PRO3 (in green); (C) merge of (A) and (B) sections showing a colocalization (in yellow) of the two labeling; (D, E) anti-RPHM21 antibody strongly labeled mature spermatozoa (s) in the acinus lumen with the staining present in both mitochondria and the nucleus, while no strong reaction is detected in spermatogenic cells (sc), whose nuclei are visible in green (TO-PRO3); (F) a higher magnification of mature spermatozoa clearly shows RPHM21 staining in sperm mitochondria (arrow) and the colocalization of RPHM21 with nuclear material in the sperm heads (arrowhead); (G) in eggs (with big and faint nuclei; arrows) no RPHM21 detectable staining is present, and only nuclear material is visible (in green, TO-PRO3). The smaller nuclei of somatic cells surrounding acini are also visible (arrowhead). All gonadic sections are visualized at confocal microscope. RPHM21 antibody staining in red; TO-PRO3 nuclear dye in green. Scale bars: (A–E) and (G) = 75 µm; (F) = 10 µm, inset: same scale bar as (F) corresponds to 4 µm.