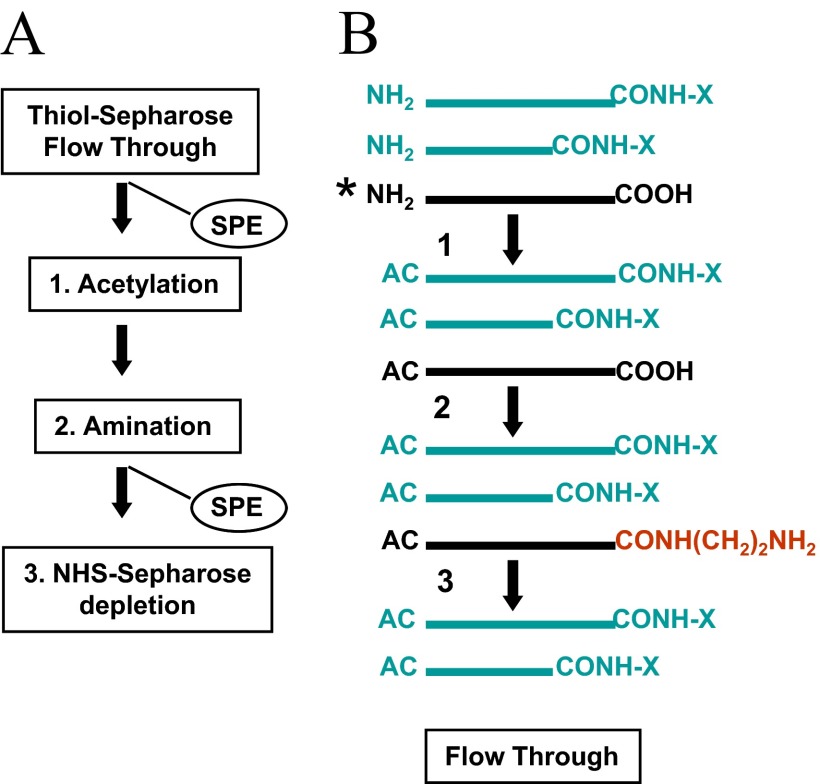
Figure 8.
Principles of sample preparation for the quantitative analysis of C-terminal truncation events. Proteins derived from different cell states are carboxyamido-methylated and subsequently, carbamidated using the light and heavy version of the nucleophile (i.e., aniline hydrochloride) in the EDC-catalyzed condensation reaction. The differentially labeled preparations are desalted and subjected CNBr cleavage. The digests are mixed and adsorbed on a C18 reversed-phase support .and carried through the sequence of chemical reaction to condition the internal/N-terminal peptides for depletion by covalent chromatography on activated thiol sepharose (see Fig. 1A). (A) Depletion of hydrolytic cleavage products. The carbamidated C-terminal peptides (and the respective truncation products), along with the subpopulation of nonspecific cleavage products bearing free carboxyl groups, are concentrated from the flow-through fraction on a C18 reversed-phase support (SPE). The immobilized material is subjected to α-amine acetylation (Step 1) and subsequently to carboxyl group amination using EDA as a nucleophile in the EDC-catalyzed condensation reaction (Step 2). By this sequence of reactions, an amino group-functionalized affinity tag is introduced selectively into the co-isolates for subsequent depletion on NHS-sepharose (Step 3). The purified C-terminal peptides (and the respective truncation products) are then analyzed by LC-tandem MS to determine their relative abundance. (B) Schematic illustration of the analyte and reaction products. AC, Acetyl group; CONH-X, carbamoyl moiety. Asterisk denotes depletion target. The amino group-functionalized affinity tag is highlighted in red.