Figure 1.
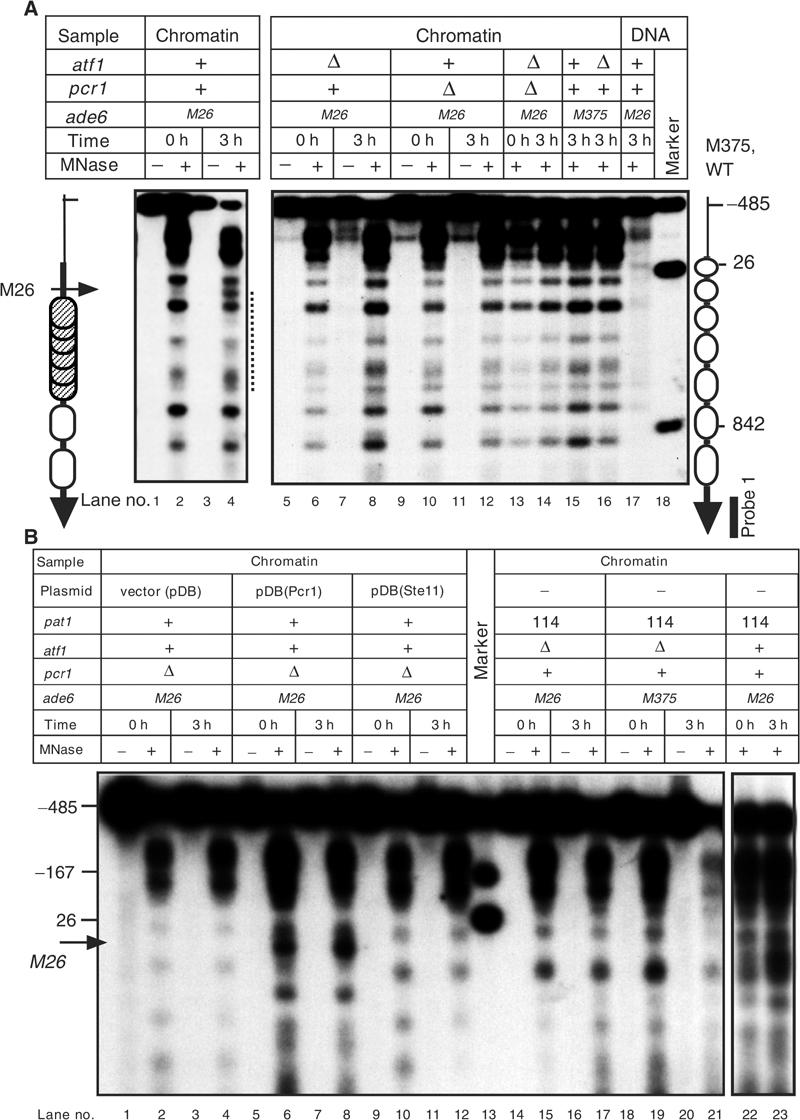
Atf1·Pcr1 is required for meiotic chromatin remodeling around ade6-M26. (A) Disruption of atf1+ or pcr1+ abolishes meiotic chromatin remodeling around ade6-M26. Diploid strains ELD205 (ade6-M26), WSP779 (ade6-M26, atf1Δ), WSP857 (ade6-M26, pcr1Δ), WSP859 (ade6-M26, atf1Δ, pcr1Δ), ELD203 (ade6-M375), and WSP780 (ade6-M375, atf1Δ) were cultured in presporulation medium (lanes 0 h). Cells were then transferred to sporulation medium and cultured further for 3 h (lanes 3 h). Chromatin isolated from cells was digested with 0 (lanes −) or 20 (lanes +) units/ml of MNase and analyzed as described (Mizuno et al, 1997). Probe 1 was used for indirect end labeling. The vertical and the horizontal arrows indicate the ade6 ORF and the position of the M26 mutation, respectively. Numbers by the right vertical arrow show the positions in nucleotides of the Xho I (−485), Bam HI (26), and Hind III (842) sites relative to the first A of the ade6 coding region. Open and hatched ovals represent phased and randomly positioned nucleosomes, respectively. The broken line by lane 4 indicates the region where the chromatin structure is remodeled. (B) Ectopically induced meiosis does not induce chromatin remodeling in atf1Δ and pcr1Δ cells. (Lanes 1–12) Chromatin structures of WSP857 (ade6-M26, atf1+, pcr1Δ) diploids harboring the empty vector (lanes vector(pDB)), the Pcr1 expressing plasmid (lanes pDB(Pcr1)), and the Ste11 expressing plasmid (lanes pDB(Ste11)) were analyzed. Experiments were performed as in Figure 1A. (Lanes 14–23) The K213 (ade6-M26, atf1Δ, pat1-114), K214 (ade6-M375, atf1Δ, pat1- 114), and GP1725x (ade6-M26, pat1-114) cells were cultured for 24 h in presporulation medium (lanes 0 h). Cells were transferred to sporulation medium and cultured at 34°C for 3 h (lanes 3 h). Chromatin analyses were performed as in Figure 1A. Overexpression of Pcr1 caused chromatin remodeling in premeiotic cells (lane 6). This may be due to artificial activation of chromatin remodeling by enhanced binding of Atf1·Pcr1 to the M26 site.
