Figure 2.
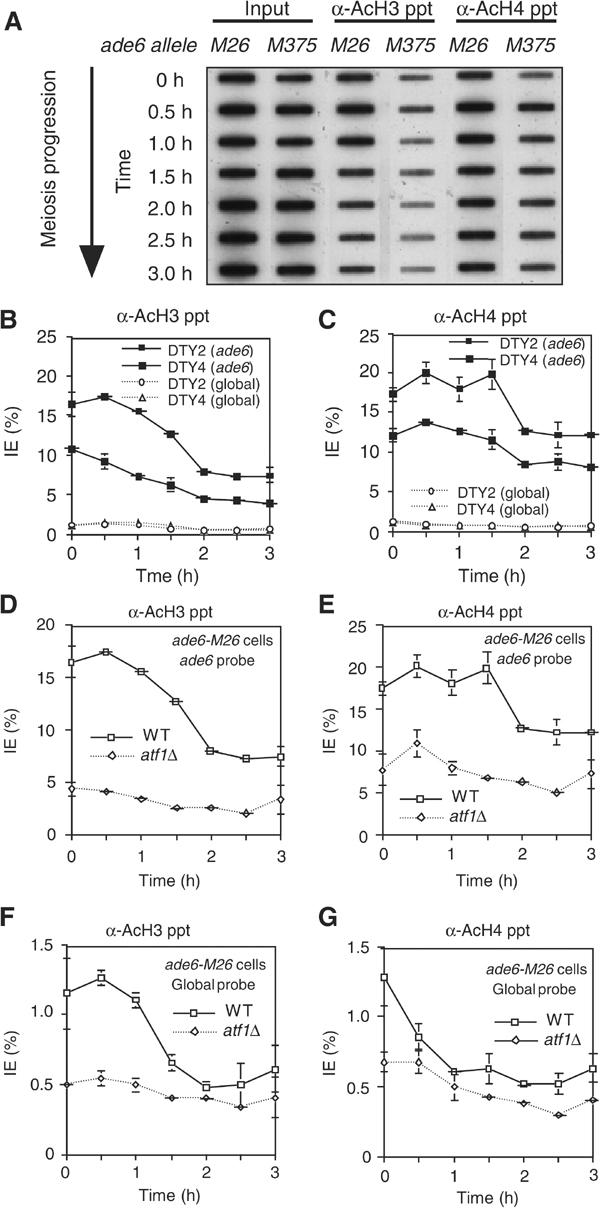
Histones H3 and H4 around ade6-M26 are highly acetylated in an Atf1-dependent manner during meiosis. Chromatin obtained from DTY2 (ade6-M26), DTY4 (ade6-M375), and WSP779 (atf1Δ, ade6-M26) diploid cells was immunoprecipitated with antiacetylated histone H3 and H4 antibodies. DNA obtained from input and immunoprecipitated material was applied to slot blots. (A) Example of primary data showing autoradiograms of slot blots probed for the ade6-M26 or ade6-M375 region. (B–G) Quantitative data are expressed as the ratio of the bound to the input material (immunoprecipitation efficiency: IE). All data were averages of at least three independent experiments. Labels inset into each figure panel indicate the relevant cell genotype and the probe used for each experiment. The data for WT in panels D–G are the same as those in panels B, C (solid line) and B, C (broken line). (B, C) Effects of ade6 alleles on acetylation of histone H3 and H4, respectively. (D, E) Requirement for Atf1 in histone H3 and H4 acetylation at ade6-M26, respectively. (F, G) Role of Atf1 in global (genome average) acetylation of histone H3 and H4, respectively.
