Figure 7.
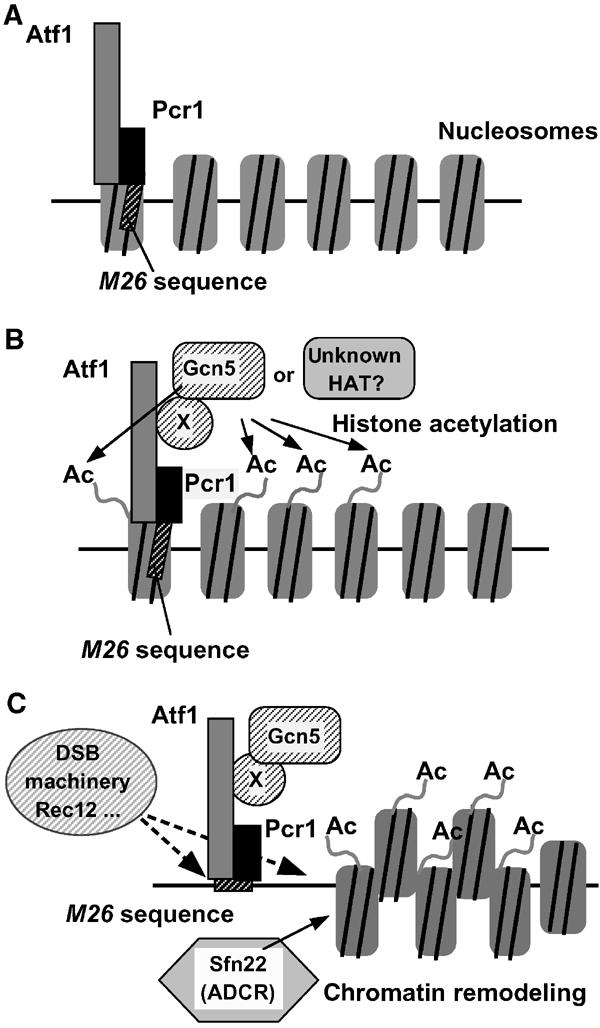
A regulatory model of meiotic recombination at M26 by HAT-mediated chromatin remodeling. (A) In cells lacking Gcn5 HAT, the histones around M26 are supposed to be hypoacetylated. In this situation, chromatin remodeling and subsequent DSB breaks occur very slowly. (B) Histones around M26 are hyperacetylated by Gcn5 HAT and possibly other HATs, which are introduced to the M26 site via the interaction with the Atf1·Pcr1 protein complex and a putative adaptor protein (shown as protein X). (C) Acetylated histones may be preferential targets of other ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling proteins (ADCR), such SpSnf22. DSB machinery, such as Rec12, is recruited to the open chromatin region created around M26, thereby activating meiotic recombination locally.
