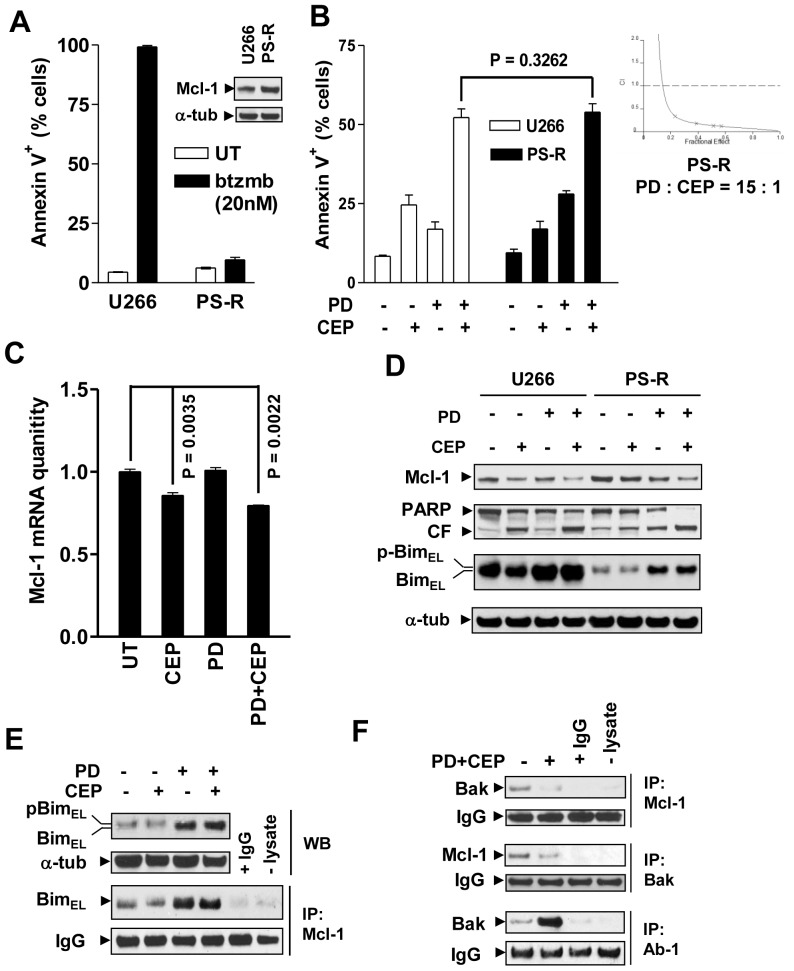
Figure 3. Bortezomib-resistant MM cells exhibiting Mcl-1 up-regulation and Bim down-regulation does not display cross-resistance to PD184352/CEP3891.
(A) Parental U266 cells and their bortezomib-resistant counterparts (PS-R) were exposed to 20 nM bortezomib (btzmb) for 24 h, after which the percentage of apoptotic cells were determined by Annexin V staining and flow cytometry. Western blot analysis was performed to monitor Mcl-1 protein (inset). (B) U266 and PS-R cells were treated with 500 nM CEP3891±7.5 µM PD184352 for 48 h, after which the extent of apoptosis (Annexin V+ cells) was determined by flow cytometry. PS-R cells were exposed to a range of concentrations of CEP3891±PD184352 at a fixed ratio (1∶15) for 48 h, after which median dose effect analysis was used to characterize the nature of the interactions using cell death (7AAD+) as an endpoint (inset). (C) and (D) Alternatively, following treatment with 500 nM CEP3891±7.5 µM PD184352, real-time qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis were performed to monitor Mcl-1 mRNA levels (16 h, C) and expression of the indicated proteins (40 h, D). (E) and (F) In parallel, following 42 h-exposure to 500 nM CEP3891±7.5 µM PD184352, PS-R cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) followed by Western blotting to assess interactions between Mcl-1/Bim (E) and Mcl-1/Bak (F, upper), or Bak conformational change (F, lower). WCL was loaded to monitor protein levels. For analyses of flow cytometry and real-time qRT-PCR, values represent the means and SD for three separate experiments.