Figure 1.
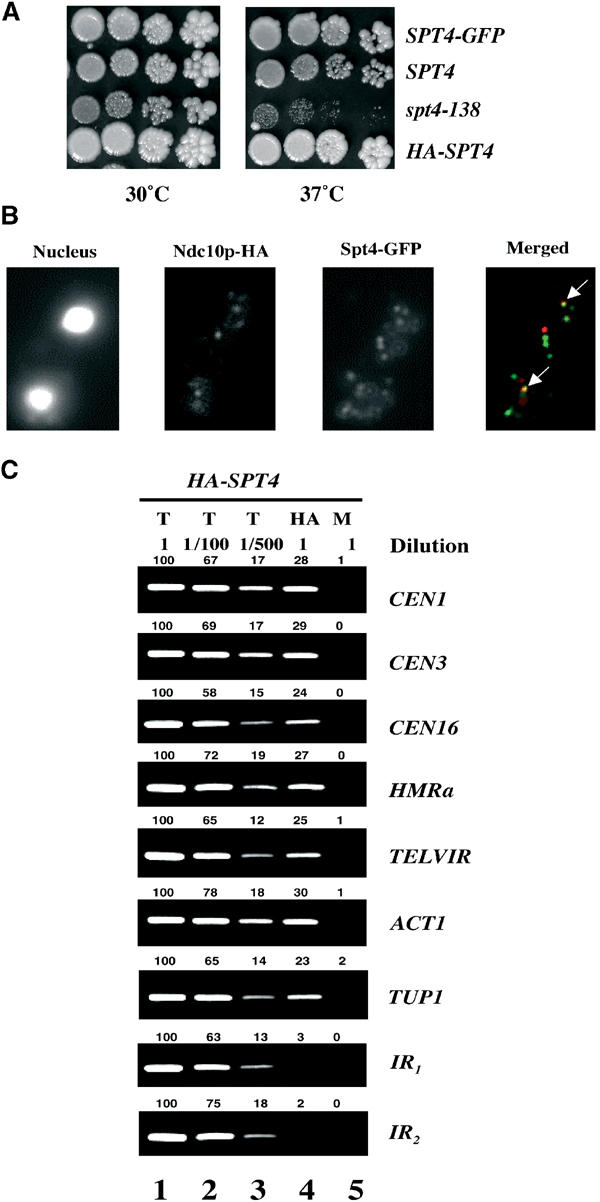
Spt4p co-localizes with kinetochores and associates with chromosomal loci. (A) Epitope-tagged SPT4 is functional. Growth of five-fold dilutions of wild-type (YPH499) and spt4-138 (YMB54) strains was compared to SPT4-GFP (YMB1859) and HA-SPT4 (GHY262) strains on YPD plates incubated at 30°C and 37°C for 3–4 days. The spt4-138 strain exhibits a slower growth compared to the wild-type strain even at the permissive temperature of 30°C. (B) Subset of Spt4-GFP foci co-localizes with kinetochore. Chromosome spreads from strain (YMB1859) expressing Ndc10p-HA, and Spt4-GFP probed with anti-GFP or anti-HA antibodies. The arrows in the merged panel indicate co-localization of Ndc10p-HA (red), and Spt4-GFP (green) is shown in yellow. (C) HA-Spt4p associates with chromosomal loci. ChIP experiments were carried out using wild-type strain (GHY262) expressing chromosomally tagged HASPT4 grown to logarithmic phase at 30°C. Different dilutions of chromatin samples from total (T) (undiluted, 1/100, 1/500), immunoprecipitated with anti-HA (HA), and mock (M) were analyzed using primers for core CEN1, core CEN3, core CEN16, HMRa, TELVIR, and ACT1 or intergenic regions (IR1 and IR2) devoid of ORFs (chromosome IV, co-ordinates 1 157 000–1 157 200 and 1 523 000–1 523 180, respectively). Values for the quantitation of the data are shown above each of the lanes, with the value for undiluted total set to 100 for each row (lane 1). These data show that the PCR yield is proportional to the amount of starting material.
