Figure 1.
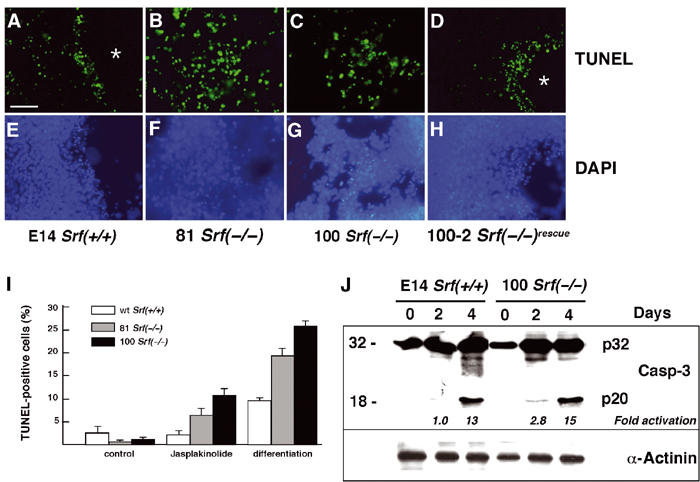
Srf(−/−) ES cells display increased apoptosis when differentiated under monolayer conditions. (A–H) ES cells of the indicated Srf genotype were grown on coverslips and differentiated under monolayer conditions for 4 days. Apoptotic cells were visualized by TUNEL staining (A–D). The same slides were counterstained with DAPI (E–H). Asterisks indicate cavity-like regions that formed exclusively in SRF-containing cells after 4 days of differentiation. Bar=50 μm. (I) ES cells of the indicated Srf genotype were grown for 48 h in the presence of LIF, followed by the addition for 24 h of either solvent (MeOH; control) or 10 nM jasplakinolide. Alternatively, cells were differentiated upon LIF removal under monolayer conditions for 4 days. Apoptotic cells were quantified by TUNEL staining followed by FACS analysis. Values represent the mean of two (differentiation) or three (jasplakinolide) independent experiments ±s.d. (J) E14 Srf(+/+) and 100 Srf(−/−) ES cells were differentiated as monolayer cultures for up to 4 days, and protein extracts were prepared after 0, 2, and 4 days. Western blotting was performed with an antiserum recognizing both the inactive caspase-3 precursor (CPP32; p32) and the active cleavage product (p20). Fold activation of caspase-3 activity, as indicated on the bottom of the blot, was calculated by dividing the normalized intensity of the respective p20 band by the normalized intensity of the p20 band at day 0. Normalized intensities were first derived by dividing the p20 signal by the respective signal from the loading control (α-actinin).
